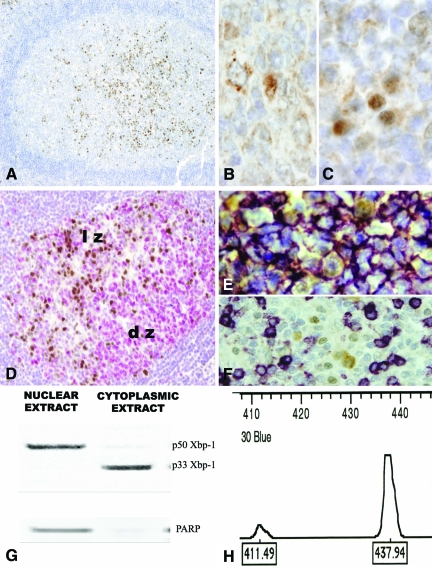
Figure 1.
Xbp-1 Expression in reactive lymphoid tissue. Human tonsil. A: In the light zones of secondary lymphoid follicles clusters of nuclear Xbp-1 positive cells can be easily identified (×10). B: The cytoplasmic Xbp-1 is ubiquitously expressed in the cytoplasm of B-cells with a granular and paranuclear pattern (×60 under oil). C: Some cells with plasmacytic features exhibit a strong nuclear positivity of Xbp-1 (×60 under oil). D: Ki-67 positive cells (red) are found in the dark zone of the germinal centers. Ki-67 negative cells in the light zone are positive for nuclear Xbp-1(brown) (×20). E: Double staining for CD20 (purple) and Xbp-1(brown) showed that cells with nuclear Xbp-1 expression are B-cells. F: T cells stained with CD3 (purple) are negative for nuclear Xbp-1(brown). G: Western-blot on compartmental protein extracts showed the unspliced p33 in the cytoplasmic extracts and the p50 protein in the nuclear extracts. A nuclear protein, PAARP was used to assed the quality of the extracts. H: Reverse transcription-PCR flanking the splicing region reveals a two peaks pattern in the Gene Scan. A main 437bp unspliced expression is in agreement with the immunohistochemical results. lz: light zone of the germinal center; dz: dark zone of the germinal center.