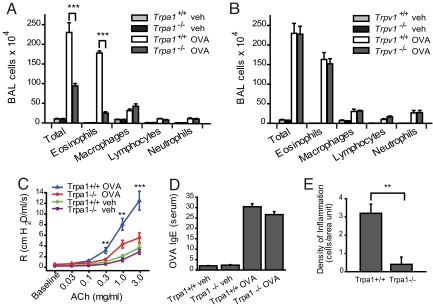
Fig. 1.
Decreased inflammatory response to inhaled OVA in TRPA1-deficient mice. (A) Reduced leukocyte infiltration in airways of OVA-challenged Trpa1−/− mice. Cell differentials are shown for total cells, eosinophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, and neutrophils in BALF collected from vehicle (veh, PBS)- and OVA-challenged Trpa1+/+ and Trpa1−/− mice. Animal groups: Trpa1+/+ OVA: n = 8, Trpa1−/− OVA: n = 8, Trpa1+/+ veh: n = 7, Trpa1−/− veh: n = 6. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001. (B) Normal inflammatory leukocyte infiltration in OVA-challenged Trpv1−/− mice. BALF leukocyte cell differentials are shown for vehicle (veh, PBS)- and OVA-challenged Trpv1+/+ and Trpv1−/− mice. Animal groups: Trpv1+/+ OVA: n = 6, Trpv1−/− OVA: n = 4, Trpv1+/+ veh: n = 6, Trpv1−/− veh: n = 4. (C) Comparison of airway resistance (R) in OVA-challenged Trpa1+/+ (blue) and Trpa1−/− mice (red), as well as vehicle (veh)-treated Trpa1+/+ (green) and Trpa1−/− (purple) mice, measured by forced oscillation in response to increasing dosages of acetylcholine. Animal groups: Trpa1+/+ OVA: n = 4, Trpa1−/− OVA: n = 4, Trpa1+/+ veh: n = 6, Trpa1−/− veh: n = 6. (∗, α = 0.05; ∗∗, α = 0.01; ∗∗∗, α = 0.001). (D) Induction of OVA-reactive Ig E in OVA-challenged wild-type and TRPA1-deficient mice, as determined by ELISA. Animal groups as in Fig. 1A. (E) Density of inflammation in H&E-stained airway sections from OVA-challenged Trpa1+/+ and Trpa1−/− mice, scored by counting of inflammatory cells near bronchial bundles (n = 4 mice per group).