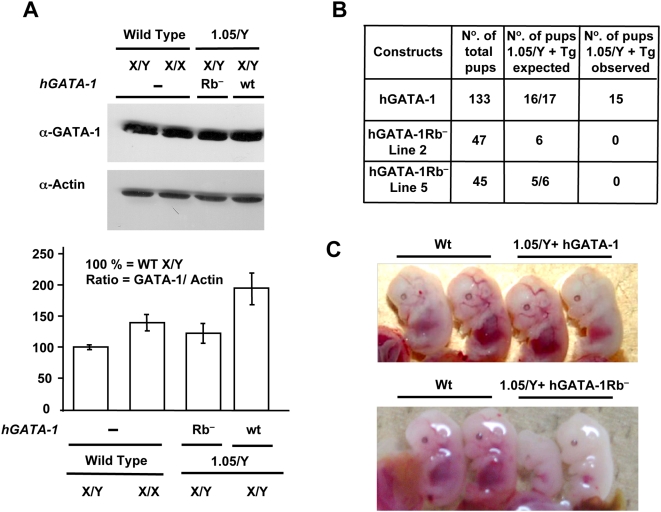
Figure 6. GATA-1/pRb interaction is necessary for terminal erythropoiesis in vivo.
(A) Comparative levels of GATA-1 proteins in fetal livers of E12.5 wt or transgene-expressing mouse embryos. Top, fetal livers from one wt male (X/Y) and one wt female (X/X) E12.5 embryos as well as from two males GATA-1.05/Y (referred to as “1.05/Y” in the figure) transgenic for either hGATA-1 (referred to as “wt” in the figure) or hGATA-1Rb− (referred to as “Rb−” in the figure). Nuclear extracts were subjected to western blot analysis using an α-GATA-1 Ab and reprobed with an anti–β-actin (α-Actin) Ab (AC-15 clone; Sigma). Bottom, GATA-1 protein levels were quantified by chemiluminescence (Intelligent Dark box, LAS-3000, Fujifilm) and normalized for β ˜-actin protein levels (n = 3). Results are expressed as means±standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. (B) Crossbreeding of XGATA-1.05/X female mice with transgenic male mice expressing hGATA-1 or the mutant hGATA-1Rb− proteins results in four possible genotypes with or without the transgene. Since the GATA-1 gene is located on the X chromosome, hemizygous XGATA-1.05/Y mice die in utero. The expected (if the transgene was resulting in complete rescue) and the observed pup number of XGATA-1.05/Y mice harboring the transgenes are indicated. (C) Top, fetal livers from E13.5 GATA-1.05/Y+hGATA-1wt control embryos (referred to as “1.05/Y+hGATA-1wt” in the figure) show an indistinguishable appearance from their wt littermates (Wt), and viable pups were born with the expected Mendelian distribution. Bottom, in contrast, GATA-1.05/Y+hGATA-1Rb − embryos in lane 5 (referred to as “1.05/Y+GATA-1Rb−” in the figure) are pale comparatively to their wt littermates (Wt) and die in utero.