Fig. 4. Intron 1 contains elements driving expression in photoreceptors.
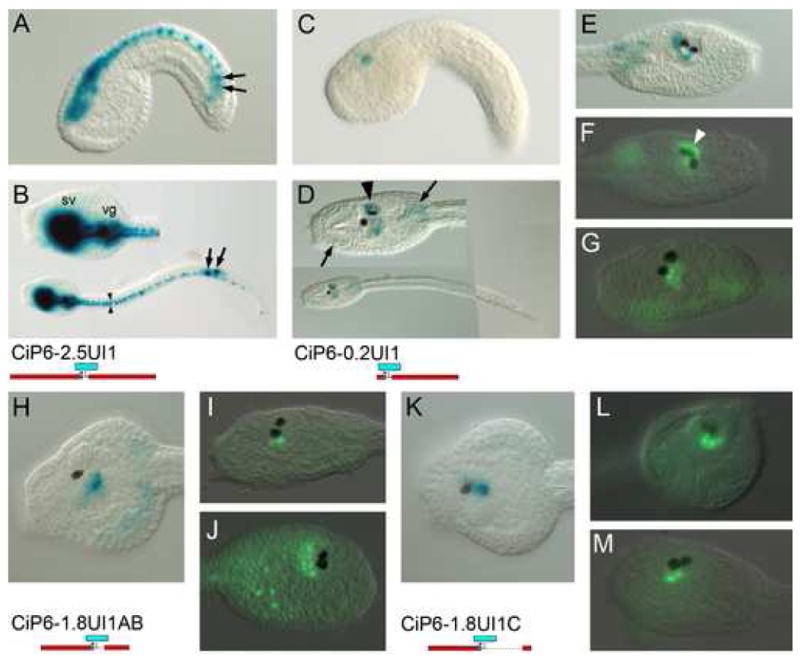
β-gal histochemistry (A-E, H, K) and anti-β-gal immunofluorescent detection (F, G, I, J, L, M) of lacZ reporter transgenes. Constructs are identified below and to the left of corresponding images. (A, C) are mid-tailbud stage in lateral view. Others are late tailbud stages in lateral views, except B, D and K, which are dorsal views, and L which is frontal. (A, B) Construct with 2.5 kb. upstream region and entire intron 1. Expression is in entire CNS, as well as ectopic expression in lineage A8.16 muscle cells (arrows) as seen in Fig. 3. Note expression in bilateral ranks of caudal nerve cord cells (arrowheads) (C-G) Intron 1 fragment connected with 200 bp. of basal promoter sequence. Expression is in the central sensory vesicle (arrowheads). Ectopic expression is also in trunk mesenchyme (arrows). In (F) note expression in photoreceptor array associated with the ocellus (white arrowhead).(H-J) Expression driven from the proximal 1 kb. of intron 1 sequence containing the I1A and I1B CNEs. Variable β-gal signal is seen in ventral and caudal portions of the central sensory vesicle. (K-L) Expression driven from the distal 300 bp. of intron 1 containing the I1C CNE. Variable β-gal signal is in similar regions to that driven by the proximal intron 1 fragment.
