Fig. 5. Intron 4 sequence downregulates expression in the neck and visceral ganglion.
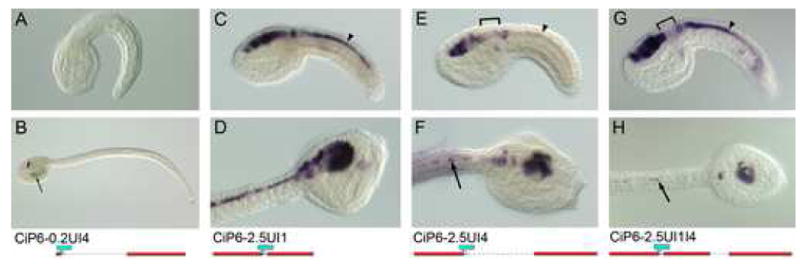
Whole mount in-situ hybridization using a lacZ antisense riboprobe, except A and B, which are β-gal histochemical staining. Transgene name and diagram are located below each embryo pair. Top row (A, C, E, G) are mid-tailbud stages, and second row are lateral (B, D, H), or dorsolateral (F) views of late tailbud stages. (A, B) Intron 4 alone drives only ectopic expression in trunk mesenchyme at late stages (arrow). (C-H) LacZ transcript expression is shown for reporter transgenes with upstream and Intron 1 sequence (C, D), upstream and Intron 4 sequence (E, F), and upstream and Intron 1 and Intron 4 sequence (G, H). Note that expression becomes downregulated in the neck and anterior visceral ganglion in the transgenes incorporating intron 4 sequence (brackets). Expression in the caudal nerve cord is reduced in E, F compared with constructs incorporating Intron 1 (C, D & G, H) (arrowheads). However at late stages (H) Intron 4 sequence represses nerve cord expression even in the presence of Intron 1 (arrows). Refer to Table 1 for scoring of multiple embryos for each transgene.
