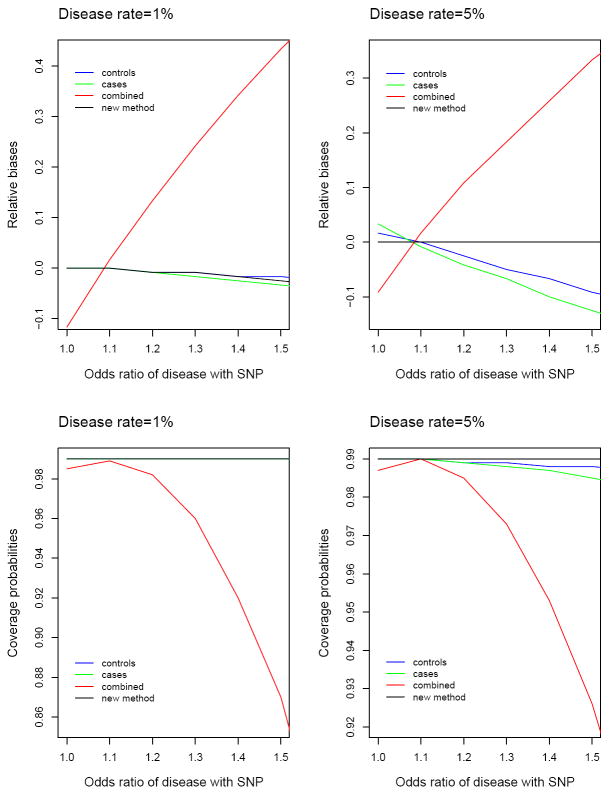
Figure 1.
Relative biases of effect estimates and coverage probabilities of 99% confidence intervals for four analysis methods: least-squares methods based on controls only, cases only and combined sample of cases and controls versus the new method. The relative bias is the bias divided by the effect size. The odds ratio of disease with the SNP (i.e., eγ1) was varied from 1 to 1.5 with 0.1 increment. Each result is based on 1,000,000 simulated data sets. For disease rate of 1%, least-squares methods based on controls only and cases only and the new method all yield coverage probabilities of virtually 99% at all values of the odds ratio of disease with the SNP, so the three curves are indistinguishable.