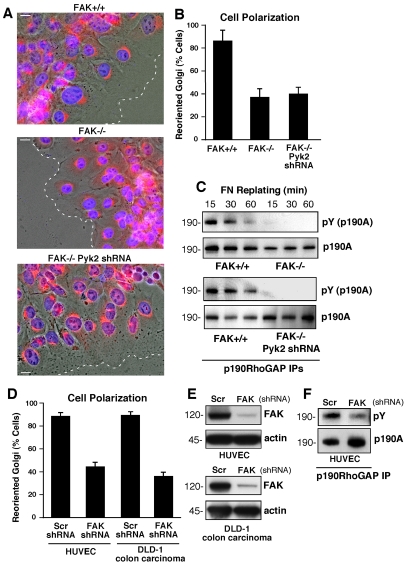
Fig. 1.
FAK promotes cell polarity and is required for p190A tyrosine phosphorylation after FN plating. (A) FAK+/+, FAK–/– and FAK–/– Pyk2-shRNA MEFs were grown on FN-coated coverslips. Cells were wounded and allowed to migrate in the presence of serum for 4 hours. Cells were fixed, imaged in phase, and stained for Golgi (β-Cop, red) and nuclear (Hoechst, blue) markers. The position of the leading lamella (broken line) is indicated. Scale bars: 15 μm. (B) Golgi reorientation analyses, a square was drawn over cell nuclei at the wound edge and divided into quadrants. Reoriented Golgi was scored positive by β-Cop staining entirely within the quadrant facing the leading edge. In total, 100 cells were analyzed; data is percent of cells analyzed ± s.d. (C) p190A immunoprecipitations (IPs) were made from FAK–/–, FAK+/+ and FAK–/– Pyk2-shRNA lysates of serum-starved cells held in suspension for 1 hour and replated onto FN-coated dishes for the indicated times. p190A IPs were sequentially analyzed by anti-phosphotyrosine (pY) and anti-p190A immunoblotting. (D) HUVEC and DLD-1 carcinoma cells expressing scrambled (Scr) or anti-FAK shRNA were analyzed for Golgi reorientation after scratch wounding as above. In total, 100 cells lining the wound edge were scored (± s.d.). (E) FAK expression is reduced by anti-FAK compared with Scr shRNA as determined by immunoblotting. (F) p190A IPs from lysates from HUVECs expressing Scr or anti-FAK shRNA that were replated onto FN-coated dishes (30 minutes) and analyzed by anti-phosphotyrosine (pY) and anti-p190A immunoblotting.