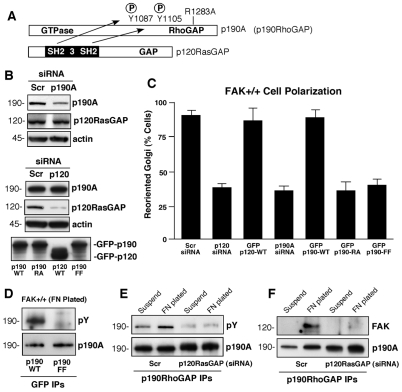
Fig. 2.
p120RasGAP promotes FN-stimulated p190A tyrosine phosphorylation, FAK association with p190A and cell polarity. (A) Schematic of the p190A and p120RasGAP proteins, and p120RasGAP SH2-mediated binding to phosphorylated Y1087 and Y1105 in p190A. R1283A (RA) mutation disrupts p190A GAP activity. (B) Scrambled (Scr)-, p190A- or p120RasGAP-siRNA transfection of MEFs and the associated protein levels after 48 hours. Actin levels were used as a control. Anti-GFP immunoblotting was used to confirm transient GFP–p190-WT, GFP–p190-RA, GFP–190-FF (Y1087F, Y1105F) and GFP-p120RasGAP expression. (C) Golgi reorientation after scratch wounding was performed with Scr p190A siRNA or p120RasGAP siRNA with siGlo co-transfection as a marker to detect transfected MEFs. Data is the percentage of 100 cells analyzed and is combined with similar analyses of MEFs transfected with GFP-p120RasGAP, GFP-p190A-WT, GFP-p190A-RA, or GFP-p190A-FF. Values are from 100 cells ± s.d. (D) Mutation of p190A Y1087F and Y1105F (p190A-FF) blocks FN-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation as determined by transfection, anti-GFP-tag immunoprecipitation (IP), and sequential anti-pY and anti-HA immunoblotting. (E) p120RasGAP siRNA-knockdown disrupts p190A tyrosine phosphorylation. Lysates from MEFs in suspension or FN plated (30 minutes) were analyzed by anti-p190A IPs followed by anti-pY and anti-p190A immunoblotting. (F) p120RasGAP siRNA-knockdown disrupts FAK-p190A association upon FN plating. Lysates from MEFs in suspension or FN plated (30 minutes) were analyzed by anti-p190A IPs followed by anti-FAK and anti-p190A immunoblotting.