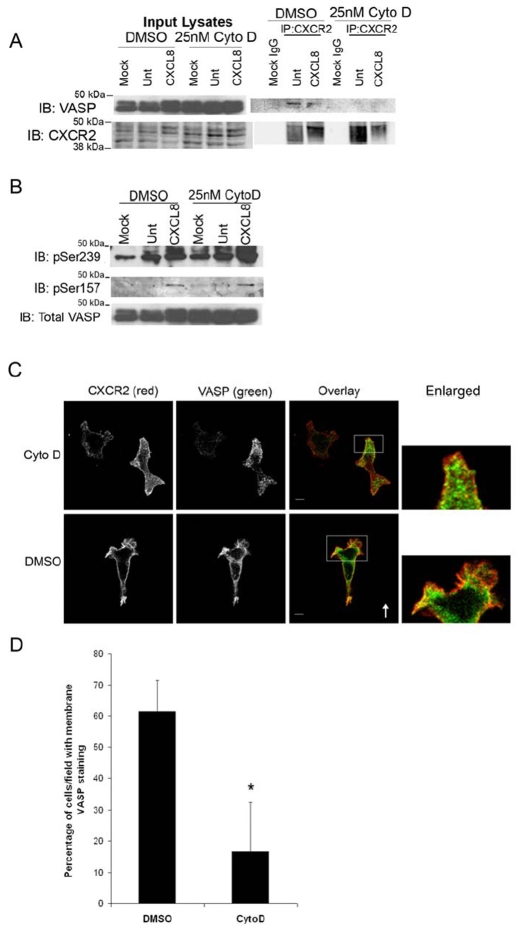
Fig. 9.
F-actin is necessary for localization of VASP to the membrane and interaction with CXCR2. dHL-60 cells were pretreated for 30 minutes with 25 nM cytochalasin D (CytoD) or DMSO (vehicle), then stimulated with vehicle (Mock, Unt) or 100 ng/ml CXCL8 for 1 minute. (A) Cell lysates were incubated with either normal rabbit IgG (Mock IgG) or rabbit anti-CXCR2 antibody-coupled Sepharose. Eluted immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blot (IB) for CXCR2 and VASP. (B) Western blot analysis (IB) using antibodies specific for VASP P-Ser157 or VASP Ser239-P of lysates. (C) Immunofluorescence confocal images of CXCR2, VASP and F-actin staining in dHL-60-CXCR2 cells and stimulated directionally with 50 ng/ml CXCL8 in Zigmond chamber for 15 minutes. The arrow indicates direction of CXCL8 gradient (0-50 ng/ml CXCL8). Image represents a single z-section of 0.49 μm. Enlarged panel images are magnified ×4 from original images. Overlay image is pseudocolored where green is VASP, red is CXCR2, and blue is F-Actin. Images were processed using Adobe Photoshop. Scale bars: 5 μm. (D) Quantification of mean ± s.e.m. percentage of cells per ×63 field exhibiting VASP immunofluorescence staining at the plasma membrane versus cytoplasm. Ten microscopic fields were examined for DMSO- and CytoD-treated cells with 2-8 cells per field Statistical significance of DMSO-versus CytoD-treated cells is indicated (*P<0.0005, Student's t-test). Data shown are representative of three separate experiments.