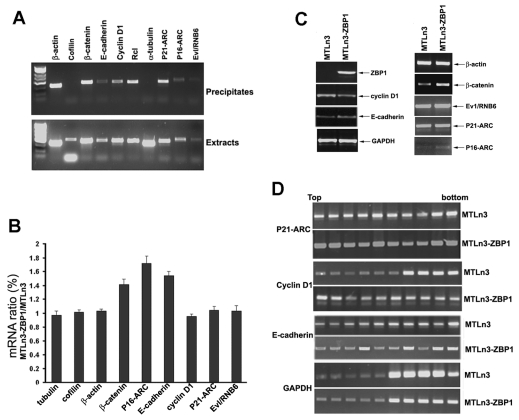
Fig. 6.
ZBP1 selectively regulates the turnover of its associated mRNAs in breast-cancer cells. (A) Anti-ZBP1 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate (IP) an MTC extract (upper panel). Total RNA, isolated from the precipitates and the cell extracts, was subjected to RT-PCR to detect the presence of ZBP1-associated mRNAs. Cofilin and α-tubulin mRNAs were used as negative controls. (B) ZBP1 selectively stabilizes its associated mRNAs in breast-cancer cells. Total RNAs were extracted from parental MTLn3 and MTLn3-ZBP1 cells after treatment with actinomycin D for 60 minutes. The relative change of indicated mRNA levels was analyzed by RT-PCR and was normalized to the corresponding α-tubulin mRNA. (C) Western blots showing the protein expression of ZBP1-bound mRNAs in MTLn3 and MTLn3-ZBP1 cells. Levels of β-catenin, P16-ARC and E-cadherin were increased, whereas the level of cyclin D1 was decreased in the presence of ZBP1. (D) Extracts of MTLn3 and MTLn3-ZBP1 cells were fractionated in 10-50% linear sucrose gradients. An equal volume of RNA from each fraction was subjected to RT-PCR for P21-ARE, cyclin-D1 and GAPDH mRNAs. Polysomal distribution of the mRNA in fractions of the sucrose gradient is shown in 1.5% agarose gels.