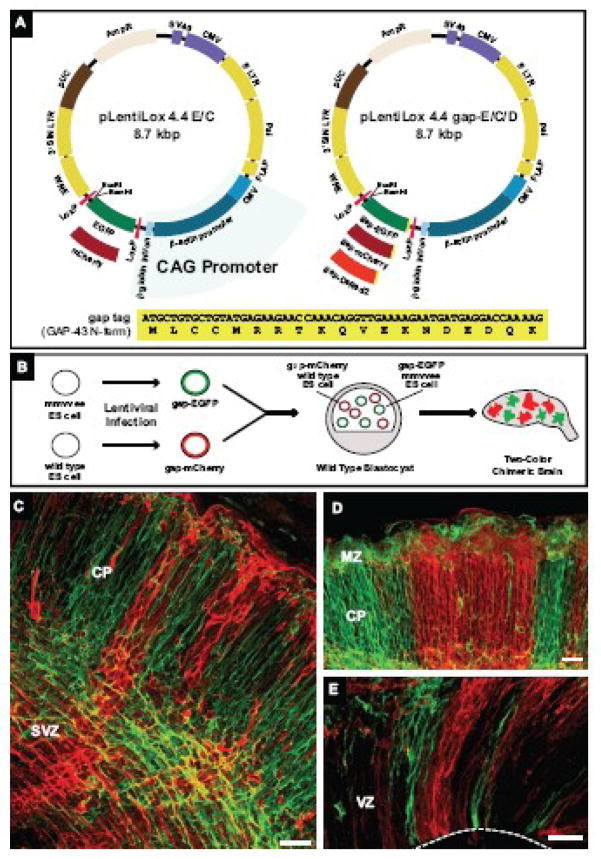
Figure 1. Lentivirus expression system for labeling cellular processes and generation of two-color chimeric embryos.
(A) Diagram of pLentiLox 4.4 and pLentiLox 4.4 gap. Expression in pLentiLox 4.4 (pLL 4.4) is driven by the CAG promoter. In pLL4.4, EGFP or mCherry (pLL4.4 E/C) is expressed downstream of the CAG promoter; fusions proteins can be created by cloning into the BamHI and EcoRI sites at the 3′ end of EGFP. The expression cassette is flanked by LoxP sites, allowing EGFP or EGFP-tagged proteins to be excised by Cre recombinase expression post-infection. To improve labeling of cellular processes in neurons, pLL4.4 was reengineered to express the first 19 amino acids of GAP-43 (shown at bottom) fused to EGFP, mCherry or DsRed2 (pLL4.4 gap-E/C/D). The N-terminus of GAP-43, referred to as a “gap” tag, contains palmitoylation sequences that target the plasma membrane.
(B) Cartoon schematic of two-color chimeric embryo generation. Wild type and Ena/VASP-null (mmvvee) ES cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing gap-EGFP and gap-mCherry, respectively, and sorted for fluorescent protein (FP) expression. FP-positive wild type and mmvvee ES cell clones were co-injected into wild type blastocysts. Brains isolated from two-color chimeric embryos contain mCherry-labeled cells derived from control cells and EGFP-labeled cells derived from mmvvee cells.
(C–E) Coronal vibratome sections from an E16.5 two-color chimeric cortex.
(C) In high percentage chimeras, most cells were labeled with either EGFP or mCherry, indicating they were derived from ES cells. Membrane-targeted FPs clearly labeled cell bodies and processes throughout the cortex. Cortical plate (CP) and subventricular zone (SVZ) are noted.
(D–E) Cortical organization in two-color chimeras. Labeling two populations of founder cells revealed the striking columnar organization of the cortex, stretching from the ventricular zone (VZ) shown in (E) to the marginal zone (MZ, in D). White dashed line in (E) marks the VZ boundary.
Scale bars for (C), (D) and (E) are 50 microns.