Figure 5. The 6-day SSI treatment reduces cholesterol accumulation in the brains and livers of young NPC1-/- mice.
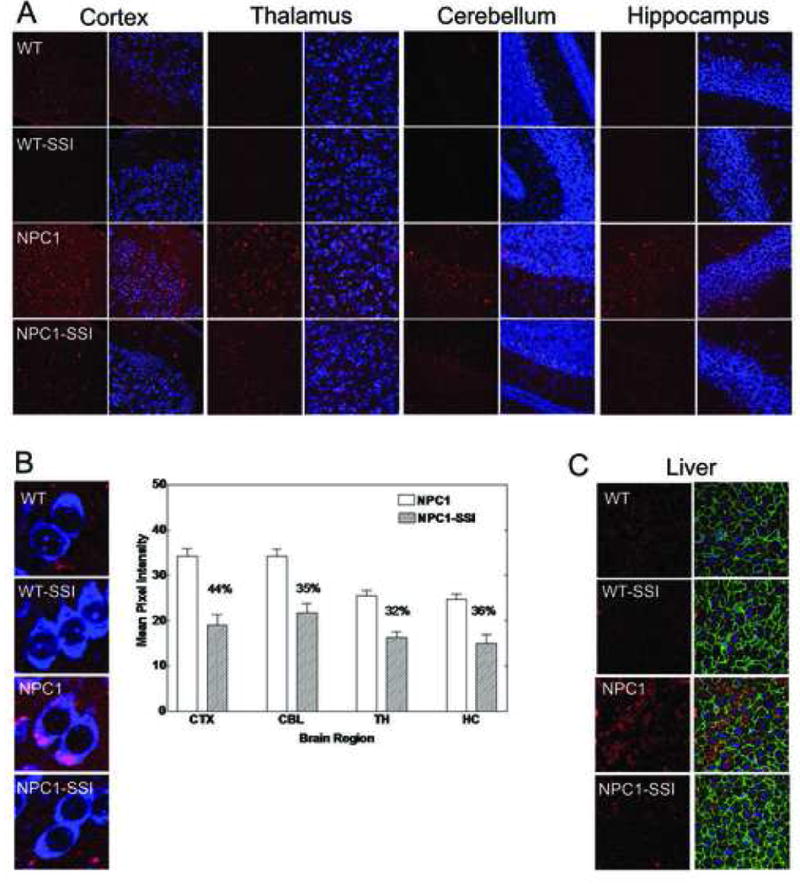
A. Neuronal cholesterol accumulation in WT and NPC1-/- mice brains with or without SSI treatment. WT and NPC1 mice received daily subcutaneous injections of CP-340868 in saline (at 10 μg/g), (WT-SSI; NPC1-SSI) or saline alone (WT; NPC1) once per day for 6 consecutive days starting at postnatal day 8. Two (NPC-/-) mice and 2 age-matched normal sibling mice (WT) were used. Afterwards, the mice (at day 14) were sacrificed and their neuronal cholesterol accumulations were evaluated by the method described previously.16 Briefly, coronal brain sections from the cortex (CTX), thalamus (TH), hippocampus (HC), and cerebellum (CBL) regions were prepared and stained with BC-theta (red) and Neurotrace (blue). Each 7 μm section was examined under a 40X objective using a Bio-Rad MRC1024 confocal microscope. The results are representative of two separate experiments.
B. Quantification of neuronal cholesterol accumulation in NPC1-/- mice brains with or without SSI treatment. The results obtained in A were quantified according to the procedures described in Materials and Methods. For each section, the reported mean pixel intensity values are values of the NPC1-/- mouse brain subtracted from values of the WT mouse. For each NPC1-/- mouse brain section, the % reduction in BC-theta signals due to SSI treatment is given. Results represent one of two separate experiments. High magnification images of representative cell types are shown at left.
C. SSI treatment reduces cholesterol accumulation in the livers of NPC1-/- mice. Livers of mice described in A were isolated and processed for staining by BC-theta according to procedure as described in Material and Methods. The green fluorescence represents plasma membrane staining using a phalloidin stain, which binds to plasma membrane F-actin. The blue fluorescence represents nuclear staining using a DAPI stain.
