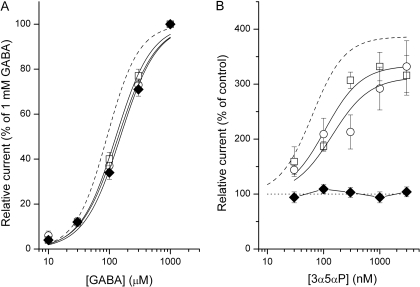
Fig. 6.
The effect of the α1Q241L mutation on the activation and modulation of concatemeric receptors. A, GABA dose-response properties for the γβαQ241L-βα (hollow circles), γβα-βαQ241L (hollow squares), and γβαQ241L-βαQ241L receptors (filled diamonds). The data show mean ± S.E.M. from 8-19 cells. The curves were fitted to the Hill equation. The best-fit parameters are: EC50 = 140 ± 13 μM, nH = 1.4 ± 0.2 (γβαQ241L-βα); EC50 = 128 ± 8 μM, nH = 1.5 ± 0.1 (γβα-βαQ241L); EC50 = 152 ± 14 μM, nH = 1.5 ± 0.2 (γβαQ241L-βαQ241L). The dashed curve applies to data from the wild-type γβα-βα receptor (reproduced from Fig. 1B). B, potentiation dose-response properties for the γβαQ241L-βα (hollow circles), γβα-βαQ241L (hollow squares), and γβαQ241L-βαQ241L receptors (filled diamonds). The data show mean ± S.E.M. from 4-6 cells. The test applications lasted 4 s and were separated from flanking control (30 μM GABA alone; ∼EC20) applications by 30 s washouts. The curve was fitted to the Hill equation with an offset (fixed at 100%). The best-fit parameters for the γβαQ241L-βα are: maximal potentiation = 313 ± 27%, EC50 = 142 ± 65 nM. The best-fit parameters for the γβα-βαQ241L are: maximal potentiation = 334 ± 28%, EC50 = 106 ± 41 nM. No fitting was attempted for the data from the γβαQ241L-βαQ241L receptor. The dashed curve applies to data from the wild-type γβα-βα receptor (reproduced from Fig. 5B).