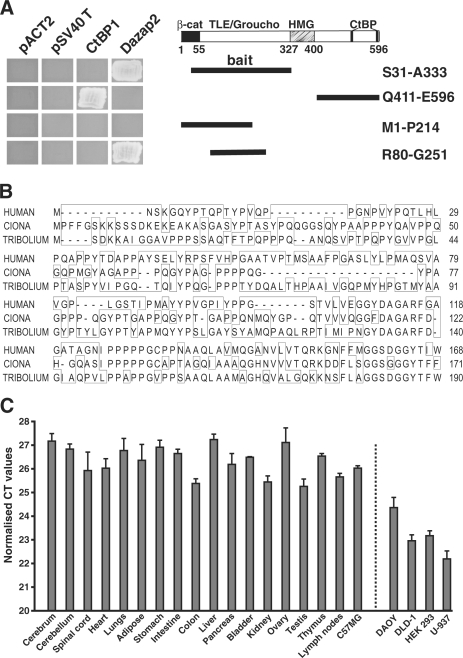
Figure 1.
Interaction between Dazap2 and TCF-4 in a yeast two-hybrid screen. (A) Deletion mutants of human TCF-4 (schematically represented on the right as thick black lines) were tested in an Y2H mini-mating assay for interaction with full-length mouse Dazap2. The left panel shows the growth of clones of yeast cells on selective agar plates. The yeast cells contain plasmids as indicated above and express TCF-4 deletion mutants that are depicted on the right. None of the TCF-4 proteins binds to the separate GAL4 activation domain (AD) encoded by ‘empty’ library vector pACT2 or to the fusion protein GAL4 AD-SV40 T large antigen (pSV40 T). β-cat, β-catenin interaction domain; TLE/Groucho, TLE/Groucho-binding domain; CtBP, CtBP-binding sites; HMG, DNA-binding domain. (B) Amino-acid comparison of human, sea squirt (Ciona) and red flour beetle (Tribolium) Dazap2. Protein sequences were aligned by the ClustalV program. The amino-acid differences are boxed. GenBank accession numbers: Homo sapiens, NP_055579; Tribolium castaneum, XP_973572; Ciona intestinalis, NM_001032667. (C) The Dazap2 gene is broadly expressed in tissues and cell lines. Results of qRT–PCR analyses performed with Dazap2-specific primers on cDNA generated from adult mouse tissues, mouse mammary epithelium C57MG cells, human medulloblastoma DAOY, human embryonic kidney HEK 293, human adenocarcinoma DLD-1 and human lymphoma U-937 cells. The reactions were performed in triplicate. The results shown are from one representative experiment from a total of two. The expression levels of Dazap2 mRNA in the indicated tissues or cell lines are presented as average CT values and the corresponding standard deviations (SD) after normalization to the levels of β-actin cDNA.