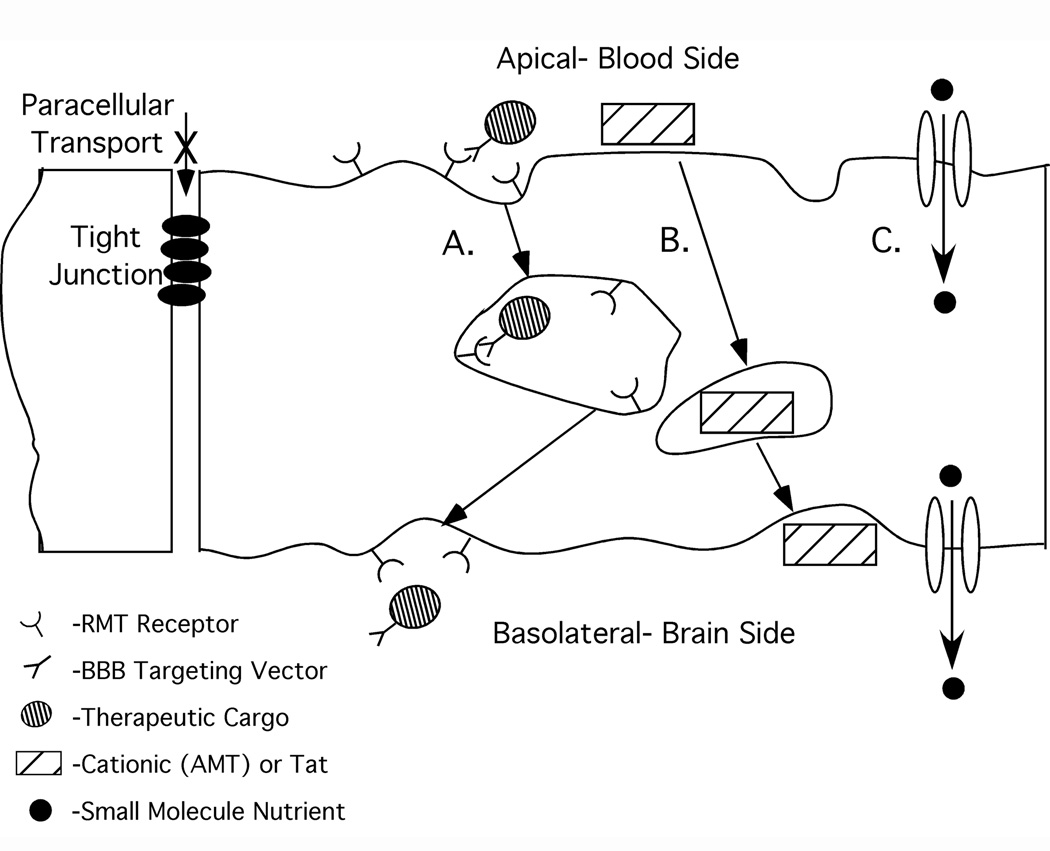
Figure 1.
Schematic of transport routes at the BBB. As a result of tight junctions closing down the paracellular space between adjacent endothelial cells, therapeutics must either diffuse through cell membranes or be transported by one of the mechanisms indicated in order to successfully reach brain tissue. A. Receptor-mediated transcytosis. B. Non-specific uptake either by cationization and absorptive-mediated transcytosis or by protein transduction domain. C. Carrier-mediated transport where nutrients enter the brain by traveling serially through transporters present in the apical and basolateral endothelial cell plasma membranes.