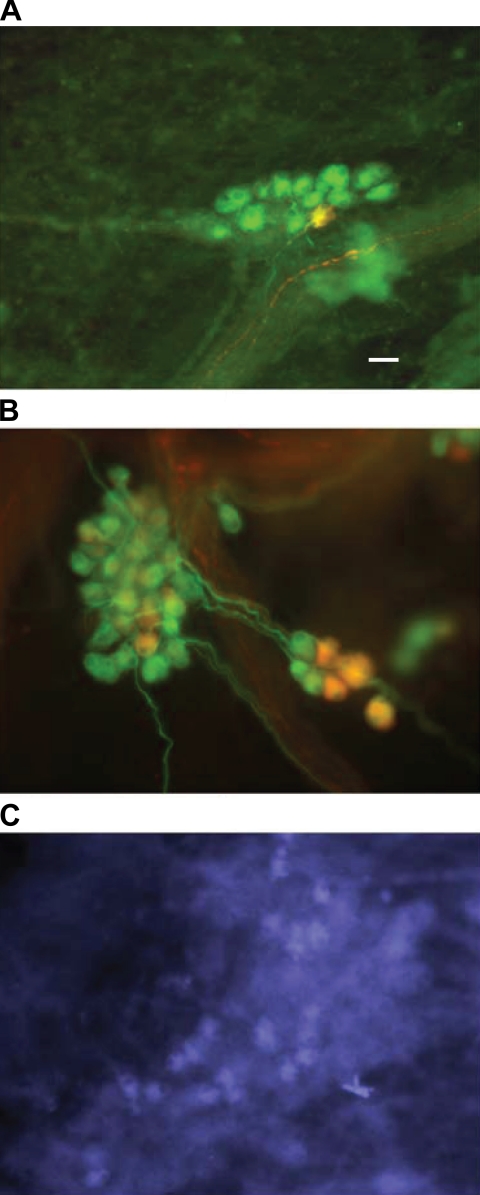
Fig. 4.
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) immunoreactivity in cardiac ganglia from control and CMI animals. Atrial intrinsic cardiac ganglia derived from control (A) and CMI (B) animals were fixed and labeled with antibodies to neuronal NOS [rabbit anti-nNOS, 1:500; and donkey anti-rabbit rhodamine (Rh), 1:500] and microtubule-associated protein 2 (mouse anti-MAP2, 1:500; and donkey anti-mouse FITC, 1:500). Merged images of the FITC and Rh immunofluorescence are shown. The percentage of nNOS-immunoreactive neurons in the untreated preparations was between 6 and 8%. The percentage of nNOS-immunoreactive neurons was significantly greater in the tissue from the CMI animals. Image in C shows inducible NOS (iNOS)-immunoreactive cells (mouse anti-iNOS, 1:100; donkey anti-mouse biotin, 1:500; and streptavidin-AMCA, 1:500) in a cardiac ganglion from a CMI animal. Scale bar, 30 μm.