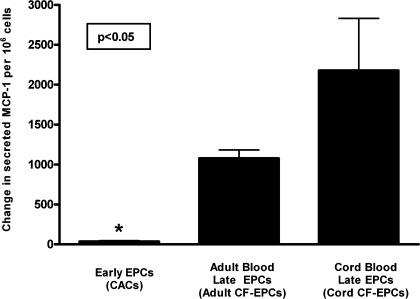
Fig. 4.
Changes in EPC paracrine activity induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. To assess whether inflammatory stimulation of EPCs could modulate their paracrine activity, EPCs were exposed to 10 ng/ml of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α during a 24-h period. The concentration of the proinflammatory chemokine MCP-1 was determined, and the change in paracrine activity was expressed as the difference in ng MCP-1 released/million cells between baseline and after TNF-α stimulation. Data are presented as means ± SE of secreted ng/million adherent cells. Statistical analysis is performed as a between-group ANOVA on the degree of change in MCP-1 release, and post hoc analysis revealed that early EPCs (n = 4) had minimal induction of MCP-1 release by TNF-α (*P < 0.05) compared with cord blood late EPCs (n = 4), whereas adult late EPCs (n = 3) had an intermediate increase in MCP-1 release.