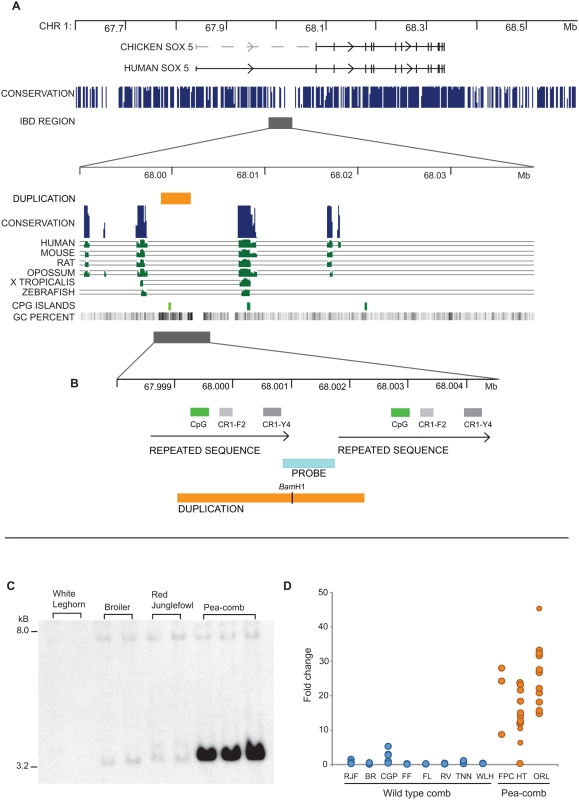
Figure 2. Identification of the Pea-comb mutation.
(A) The region on chicken chromosome 1 harbouring SOX5. The conservation score track shows the large number of Evolutionary Conserved Non-Coding Elements at the SOX5 locus. The region upstream of SOX5 exon 2 identified through IBD mapping and showing complete association to Pea-comb is marked with a dark shaded bar. Bottom part: the Pea-comb IBD region is expanded. The position of the 3.2 kb duplicated sequence in the near vicinity of non-coding sequences conserved across vertebrate species is marked with an orange bar (adapted from the UCSC genome browser http://genome.ucsc.edu/). The GC content and the location of CpG islands are indicated. (B) Localization and composition of the duplicated sequence. CR1-F2 and CR1-Y4 are partial LINEs and a small CpG island is marked with a green bar. The region corresponding to the probe used for Southern blot analysis is indicated. (C) Southern blot analysis using genomic DNA digested with BamHI from Pea-comb and wild-type chickens; the estimated sizes of restriction fragments are given to the left. (D) Results of real-time PCR analysis of the duplicated region. Individual phenotypes were not available for the Hua-Tung breed and the real-time PCR assay indicated that one bird was homozygous wild-type which is fully possible since Pea-comb is not fixed in this breed; furthermore, this bird did not carry the Pea-comb haplotype. The results for each individual sample are compiled in Table S3. RJF, red junglefowl; BR, broiler; CGP, Czech Golden Pencilled; FF, Friesian Fowl; FL, Finnish Landrace; RV, Red Villafranquina; TNN, Transylvanian Naked Neck; WL, White Leghorn; FPC, French Pea-comb; HT, Hua-Tung; ORL, Orlov.