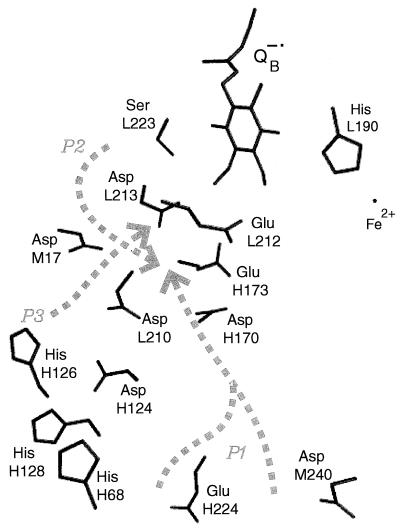
Figure 4.
Part of the RC structure near the secondary quinone, QB binding site, as determined for the QB− state by Stowell et al. (18). Possible proton transfer pathways (P1–P3) proposed by Abresch et al. (19) are shown by dashed lines. One carbonyl oxygen of QB is located near Ser-L223 and the backbone NH of Ile-L224 (not shown); the other carbonyl oxygen of QB is located near His-L190. Nearby are two carboxylic acid groups Asp-L213 and Glu-L212 that have been implicated in proton transfer to reduced QB (reactions 2a and 2b, respectively) (8–13) and to which the proton transfer pathways lead. Also shown are a His cluster (consisting of H68, H126, and H128) and a carboxylic acid cluster (consisting of Asp-L213, Asp-L210, Asp-M17, Glu-H173, Asp-H170, and Asp-M124).