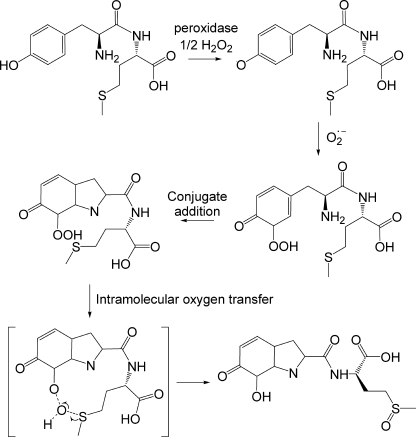
FIGURE 7.
Proposed mechanism for the formation of Tyr-Met-dioxide. The Tyr residue is oxidized in a peroxidase-mediated one-electron oxidation reaction by H2O2 to give the phenoxyl radical, which adds to superoxide to form the hydroperoxide intermediate. The hydroperoxide undergoes conjugate addition of the amine nitrogen to the Tyr ring and the Met residue is oxidized to its sulfoxide via intramolecular oxygen transfer from the Tyr hydroperoxide. The reaction is shown for the ortho hydroxyl isomer; an equivalent reaction can be written for the para form.