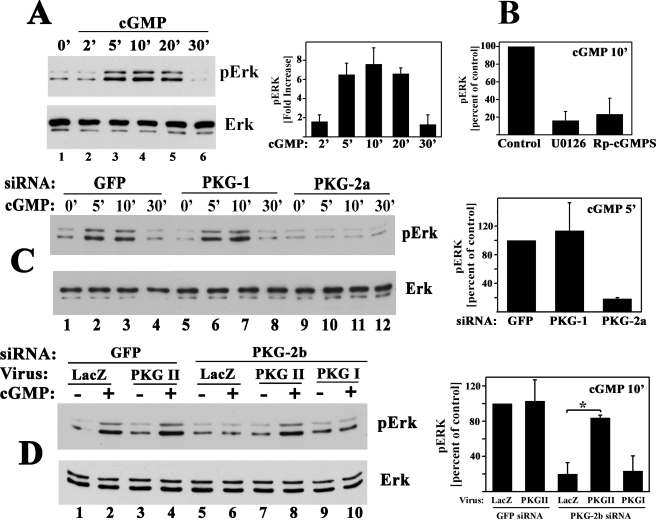
FIGURE 9.
NO/cGMP activation of PKG II is sufficient to activate Erk1/2. Erk phosphorylation was assessed in serum-deprived MC3T3 cells as described in Fig. 7A. A, cells were treated with 50 μm 8-pCPT-cGMP for the indicated times. The bar graph summarizes three independent experiments. B, cells were preincubated for 1 h in medium alone or in medium containing 10 μm U0126 or 10 μm SB203580 as indicated, prior to receiving 50 μm 8-pCPT-cGMP (cGMP) for 10 min; phospho-Erk levels in cells treated with cGMP alone were assigned a value of 100%. C, cells were transfected with a control siRNA specific for GFP (lanes 1–4), or an siRNA targeting PKG I (siRNA PKG-1, lanes 5–8), or PKG II (siRNA PKG-2a, lanes 9–12) as described in Fig. 5 and were treated with 50 μm 8-pCPT-cGMP for the indicated times. The bar graph on the right summarizes phospho-Erk1 levels measured in cells treated with cGMP for 5 min; p < 0.05 was used for the comparison between cells transfected with PKG-2a siRNA versus GFP siRNA. D, cells were transfected with either GFP siRNA (lanes 1–4) or the mouse PKG II-specific siRNA PKG-2b (lanes 5–10); 8 h later, cells were infected with control virus (LacZ, lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6), virus encoding siRNA-resistant rat PKG II (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8), or virus encoding PKG I (lanes 9 and 10). Forty eight hours later, cells were treated with 8-pCPT-cGMP for 10 min. The bar graph on the right summarizes cGMP-induced phospho-Erk1 levels; *, p < 0.05 for the comparison between LacZ and PKG II virus-infected cells transfected with PKG-2a siRNA.