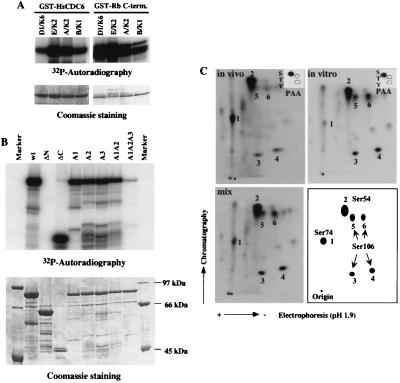
Figure 2.
HsCdc6 is a Cdk substrate. (A) Substrate specificity of cyclin-Cdk complexes against GST-HsCdc6 in comparison with a known substrate protein, GST-Rb C terminus (residues 768–928). One to 2 μg GST-HsCdc6 or GST-Rb was incubated with purified baculovirus-expressed cyclin D1-Cdk6 (D1/K6), cyclin E-Cdk2 (E/K2), cyclin A-Cdk2 (A/K2), or cyclin B1-Cdc2 (B/K1) in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography (Upper) or Coomassie blue staining (Lower). (B) The GST-HsCdc6wt and its mutant proteins described in Materials and Methods were incubated with cyclin E-Cdk2 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography (Upper) or Coomassie blue staining (Lower). (C) 32P-labeled immunoprecipitated HsCdc6 protein from cells in S/G2 described in Fig. 1B (in vivo) and GST-HsCdc6 protein phosphorylated by cyclin E-Cdk2 described in A (in vitro) were eluted from SDS/polyacrylamide gels and then digested with trypsin. The resulting phosphopeptides were separated by electrophoresis (pH 1.9 buffer) in the horizontal dimension (anode on the left) and chromatography (isobutyric acid buffer) in the vertical dimension. Shown are 2D tryptic phosphopeptide maps of: in vivo, HsCdc6 from in vivo 32P-labeled G2/M cells (2,000 cpm); in vitro, GST-HsCdc6 phosphorylated by cyclin E-Cdk2 in vitro (2,000 cpm); mix, mix of in vivo (1,000 cpm) and in vitro (1,000 cpm) and the schematic map. The major phosphopeptides, 1–6, are labeled. PAA of in vivo 32P-labeled HsCdc6 and GST-HsCdc6 phosphorylated by cyclin E-Cdk2 in vitro were performed, and radioactive phosphoamino acids were visualized by autoradiography (Insets).