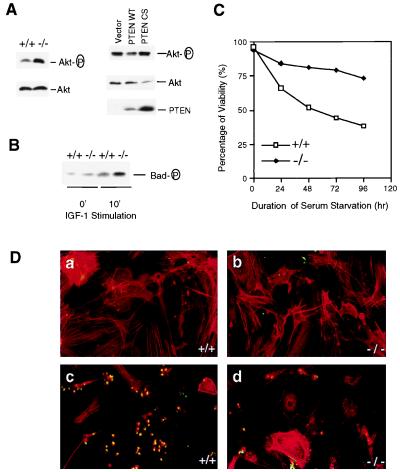
Figure 5.
Increased phosphorylation of Akt and Bad promotes Pten−/− MEF cells survival. (A, Left) MEF cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analyses as described in the legend of Fig. 4B. (A, Right) Pten−/− MEF cells were infected with retroviruses carrying empty vector, the WT PTEN, or the PTEN CS mutant. Cells were harvested 48 hr postinfection. Cell lysates (50 μg each) were subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for phospho-Akt or Akt, respectively. A duplicate filter also was analyzed with anti-PTEN antibody. (B) MEF cells were serum-starved for 16 hr, then labeled with [32P]orthrophosphate for 4 hr. Cells then were stimulated with IGF-I (1 μg/ml) for 10 min before harvest. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Bad antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. (C) Propidium iodide staining. Pten+/+ or Pten−/− MEF cells were seeded in serum-free medium. At the indicated time, cells (both adherent and in suspension) were collected and stained with isotonic propidium iodide solution. Percentage of cell viability, determined by using fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis, is presented. (D) TUNEL assay. Log-phase Pten+/+ (a and c) and Pten−/− (b and d) MEF cells were grown with (a and b) or without (c and d) serum for 72 hr. Cells were stained with TUNEL reaction mix (green) and counterstained with rhodamine-phalloidin (red). Apoptotic cells were indicated by positive staining with both TUNEL reaction mix and pholloidin dye (yellow).