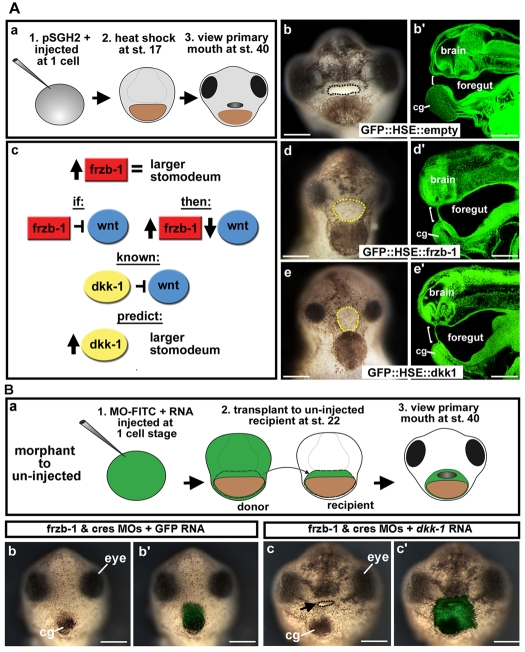
Fig. 5.
Frzb-1 and Dkk-1 regulate the same pathway. (A) Temporal overexpression of frzb-1 and dkk-1 during neurula (stage 17). b′,d′,e′ are sagittal optical sections (anterior to the left). Assayed at stage 40, two independent experiments. Open primary mouth, black dotted line; closed stomodeum, yellow dotted line; bracket indicates the position of the primary mouth or stomodeum; pSGH2, ISceI-GFP-HSE plasmid. Scale bars: 250 μm. (a) Schematic of experimental design. (b) Control (GFP::HSE) results in a normal primary mouth (90%, n=66), frontal view. (b′) Embryo treated as in b with a normal primary mouth. (c) Schematic showing the prediction that increased Frzb-1 would mimic overexpression of Dkk-1. (d) Injection of GFP::HSE::frzb-1 results in a larger stomodeum, frontal view (48%, n=50). (d′) Embryo treated as in d, showing increased stomodeal surface. (e) Injection of GFP::HSE::dkk1 results in a larger stomodeum, frontal view (53%, n=38). (e′) Embryo treated as in e has an increased stomodeal surface. (B) Rescue of the primary mouth in frzb-1/crescent morphants with dkk-1 mRNA. Frontal views, assayed at stage 40 in duplicate. Black arrow, primary mouth; cg, cement gland. Scale bars: 250 μm. (a) Schematic of experimental design. (b) The primary mouth is absent when donor tissue is derived from embryos injected with frzb-1/crescent morpholinos and GFP mRNA (90%, n=10). (b′) Overlay of b with FITC fluorescence, indicating the location of the donor tissue in the recipient. (c) When donor tissue is derived from embryos injected with frzb-1/crescent morpholinos and dkk-1 mRNA, 66% of recipients form a primary mouth and 33% form a large stomodeum with no opening (n=12). (c′) Overlay of c with FITC fluorescence.