Fig. 2.
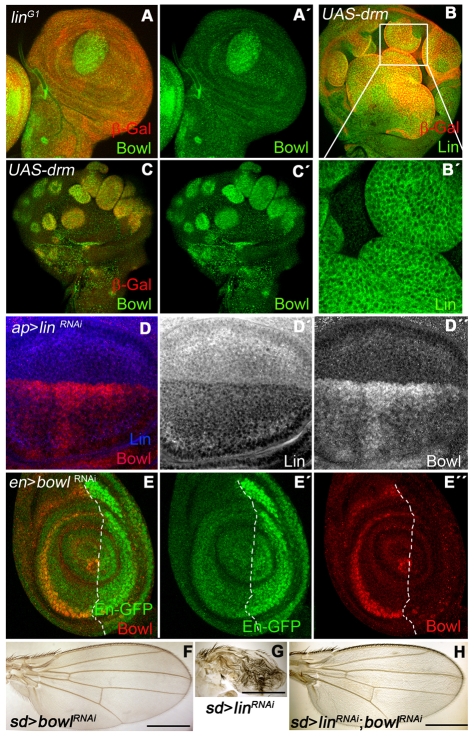
Functional interaction between Lin, Drm and Bowl in wing development. (A,A′) Bowl protein expression (green) in a wing disc containing a linG1 clone. (B,B′) Subcellular localization of Lin protein in Drm GOF clones (red in B). In a higher magnification of B, Lin protein (green in B,B′) is relocalized to the cytoplasm. (C,C′) Bowl protein stabilization (green in C,C′) in Drm GOF clones (red in C). (D-D″) ap-Gal4>UAS-linRNAi wing disc shows the absence of Lin protein (blue in D, grey in D′) and the stabilization of Bowl (red in D, grey in D″). (E-E″) en-Gal4>UAS-bowlRNAi leg disc (labeled with GFP, green in E,E′) shows absence of Bowl protein in the P compartment (red in E,E″). (F) A sd-Gal4>UAS-bowlRNAi wing with Bowl expression knocked down in the wing pouch. (G) The sd-Gal4>UAS-linRNAi wing shows a severe phenotype in terms of reduction of wing size. (H) This lin- phenotype is suppressed by co-expression of UAS-linRNAi and UAS-bowlRNAi using sd-Gal4. Scale bars: 500 μm.