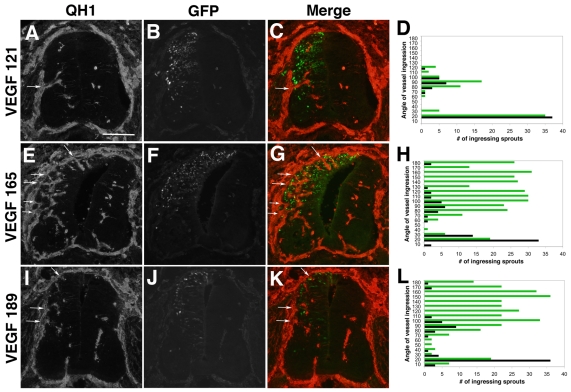
Fig. 3.
Ectopic expression of heparin-binding VEGF isoforms induces supernumerary vessel ingression points into the developing neural tube. Quail neural tubes were electroporated with hVEGF121-GFP, hVEGF165-GFP or hVEGF189-GFP DNAs (green, panels B, F, J) on day 3 (HH 16-18) and harvested 48 hours later (HH 25-26). Transverse sections were stained with QH1 antibody (red, panels A,E,I) to visualize vessels, and five embryos from each group were analyzed as described (panels D,H,L; green lines, total ingression points for ectopic VEGF-expressing sides of neural tubes at each 10° of arc; black lines, total ingression points for contralateral control sides of the neural tubes at each 10° of arc). C, G and K are a merge of red (QH1) and green (eGFP) channels. (A-C) Quail neural tubes electroporated with hVEGF121 DNA displayed a grossly normal distribution of angiogenic ingression points along the dorsoventral axis of the ectopic VEGF-expressing side of the neural tube (arrows in A,C). (D) The quantitative analysis showed no change in the distribution of ingression points for sprouts between the control (black) and VEGF121-expressing (green) sides of the neural tube, and a slight increase in the frequency of ingression points in the medial region of the VEGF-expressing side of the neural tubes (n=5 embryos). (E-G) Quail neural tubes electroporated with hVEGF165 DNA had ectopic dorsal sprouts (arrows in E,G). (H) The quantitative analysis showed increased distribution and frequency of vessel ingression points in the dorsal region of the hVEGF165-expressing side of the neural tube (green), where ectopic expression is localized (n=5 embryos). (I-K) Quail neural tubes electroporated with hVEGF189 DNA had ectopic dorsal sprouts (arrows in I,K). (L) The quantitative analysis showed increased distribution and frequency of vessel ingression points in the dorsal region of the hVEGF189-expressing side of the neural tube, where ectopic expression is localized (n=5 embryos). Scale bar: 100 μm.