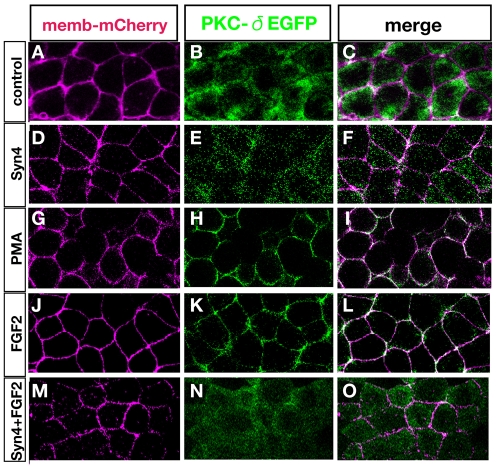
Fig. 5.
Membrane translocation of PKCδ by FGF is inhibited by Syn4. Xenopus animal caps analysed by confocal microscopy after injection/treatment as indicated. (A-C) Control animal cap shows cytoplasmic localisation of PKCδ. (D-F) Animal caps injected with Syn4 mRNA. PKCδ shows cytoplasmic distribution. (G-L) Phorbol ester (PMA; G-I) or FGF2 (J-L) triggers the translocation of PKCδ into the membrane. (M-O) Syn4 inhibits the translocation of PKCδ activated by FGF2.