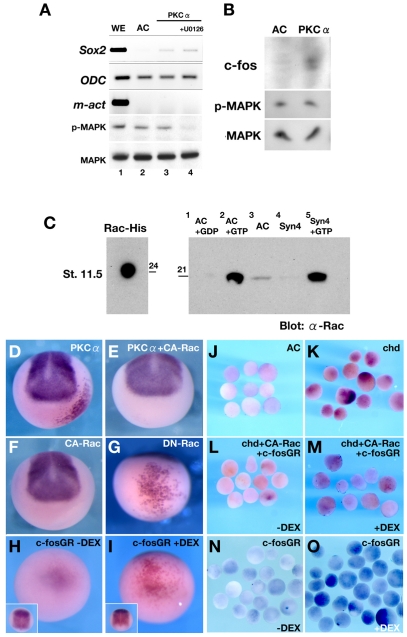
Fig. 7.
The PKC-dependent pathway of neural induction is mediated by the Rac/JNK/AP-1 pathway. (A) RT-PCR of the indicated genes using RNA from Xenopus whole embryos (WE, lane 1), animal caps (AC, lane 2), animal caps expressing PKCα (PKCα, lane 3) or animal caps expressing PKCα and treated with the inhibitor U0126 (+U0126, lane 4). Note that Sox2 is induced by PKCα even when MAPK is inhibited (lane 4). (B) Western blot of control- or PKCα-injected animal caps, detecting c-Fos, phosphorylated MAPK (p-MAPK) and MAPK. Neuralisation of the animal caps correlates with an increase in c-Fos levels, whereas p-MAPK is unchanged. (C) Rac activation assay. (Left) Rac1-His recombinant protein (24 kDa; 20 ng) was loaded and detected by anti-Rac antibody as a positive control. (Right) The same volume of reaction mix was loaded for each condition. Lane 1 (AC+GDP), negative control; lane 2 (AC+GTP), positive control that shows the total amount of Rac protein in the animal cap samples; lane 3 (AC), endogenous active Rac present in animal caps at stage 11.5; lane 4 (Syn4), endogenous active Rac present in animal caps at stage 11.5 injected with 500 pg of Syn4 mRNA (note that Syn4 abolishes endogenous Rac activity); lane 5 (Syn4+GTP), total amount of Rac protein after Syn4 injection. The experiment was repeated three times. (D-I) Whole-mount in situ hybridisation analysis of embryos injected, as indicated, into the A4 blastomere of 32-cell stage embryos. (D) Human (h) PKCα mRNA induces ectopic Sox2 expression (68%, n=92). (E) Co-injection of constitutively active Rac and hPKCα inhibits ectopic Sox2 expression (21% of induction, n=34). (F) Injection of constitutively active Rac does not induce Sox2 expression (0%, n=32). (G) Dominant-negative Rac1 mRNA induces ectopic ventral Sox2 expression (90%, n=40). (H,I) Ventral view of embryos injected with c-Fos-GR mRNA and activated with dexamethasone (DEX) at stage 10.5. Ectopic Sox2 expression is observed only after DEX treatment (I), being absent when no DEX is added (H; inset shows dorsal side). (J-O) In situ hybridisation for Sox2 in animals caps. (J) Control animal caps show no Sox2 expression. (K) Animal caps from embryos injected with chordin (chd) mRNA show Sox2 expression. (L) Animal caps from embryos injected with chordin, constitutive Rac and c-Fos-GR mRNA but without adding DEX. Activation of Rac leads to inhibition of Sox2. (M) Similar to L, but c-Fos-GR is activated by DEX treatment. Rescue of Sox2 expression is observed. (N) Injection of c-Fos-GR mRNA, but without adding DEX. (O) c-Fos-GR-injected animal caps activated with DEX show an increase in Sox2 expression.