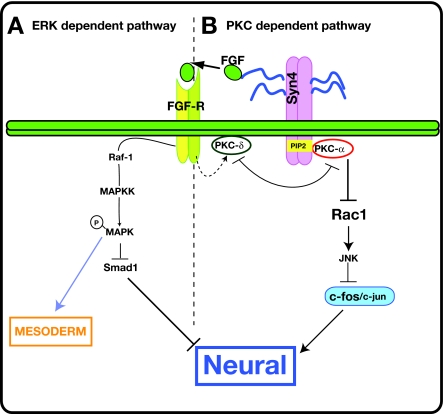
Fig. 8.
Model of neuralisation by Syn4. (A) The Syn4/ERK-dependent pathway. The glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the extracellular domain of Syn4 activate the FGF/MAPK pathway. The activation of this pathway can lead to mesoderm induction, but also contributes to neural induction, probably though the inhibition of Smad1. (B) The Syn4/PKC-dependent pathway. The intracellular domain of Syn4 inhibits PKCδ and activates PKCα. The inhibition of PKCδ is required for the recruitment of PKCα to the membrane and its binding to Syn4. Activated PKCα inhibits Rac activity. Rac activates JNK, which phosphorylates c-Jun and inhibits the formation of the c-Jun/c-Fos dimers that form part of the AP-1 transcriptional regulator complex. Thus, the inhibition of Rac by Syn4/PKCα leads to the activation of the AP-1 complex that controls the transcription of preneural genes