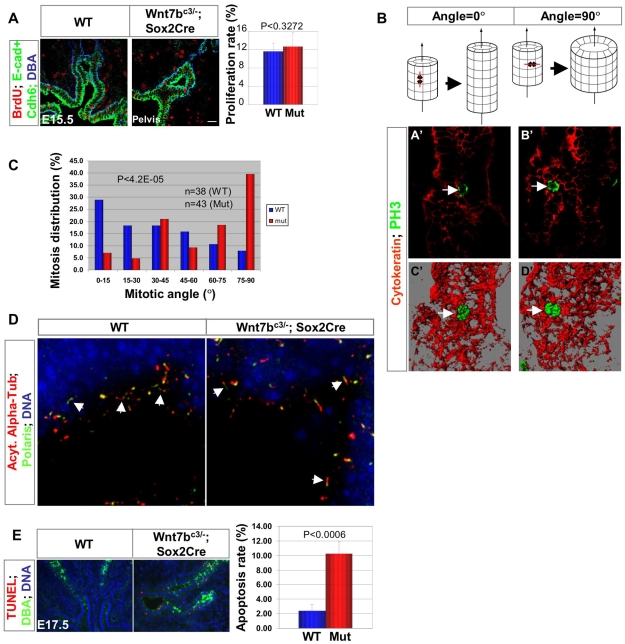
Fig. 4.
The failure to initiate renal medulla development in Wnt7b mutants reflects alterations in the plane of epithelial cell division. (A) Cell proliferation was analyzed in wild-type and Wnt7b mutant kidneys at E15.5 by pulse-labeling with BrdU. BrdU incorporation was visualized by anti-BrdU antibodies in conjunction with specific markers, as indicated, to identify specific epithelial compartments. E-Cadherin (E-cad) and cadherin 6 (Cdh6) immunostainings together with DBA lectin demarcate the cell boundaries between the nephron and collecting duct epithelia. No significant difference in the proliferation rate is observed between wild-type (n=3) and Wnt7b mutants (n=4). Scale bar: 40 μm. (B) Diagrams illustrating the effects of oriented cell division on tubule morphogenesis and three-dimensional reconstructions of optical sections showing mitotic configurations in the collecting duct epithelium. Anaphase chromosomes were visualized with phospho-histone H3 staining (PH3, green, arrow) and the collecting epithelium with pan-cytokeratin staining (red; A′-D′). Stacks of single optical sections (A′,B′) were rendered to generate 3D images (C′,D′) for the measurement of mitotic angles. (C) Histogram of mitotic angles in the prospective medullary collecting ducts of wild-type and Wnt7b mutant kidneys at E15.5. Mitotic angles were determined relative to the longitudinal axis of the perspective collecting duct epithelium delineated with pan-cytokeratin immunostaining as detailed in the Materials and methods. (D) 3D reconstruction of stacks of optical sections of acetylated α-tubulin staining demonstrate that normally sized primary cilia (arrow) were present in the collecting duct epithelia of Wnt7b mutants. Moreover, the intraflagellar transport protein Polaris localized to the primary cilium as expected. (E) Apoptosis was compared by TUNEL analysis (red) in the collecting duct epithelium (DBA lectin, green) of kidney sections from wild-type and Wnt7b mutant embryos at E17.5. The apoptosis rate increased markedly and significantly in Wnt7b mutants (n=4) relative to in wild-type controls (n=4).