Fig. 1.
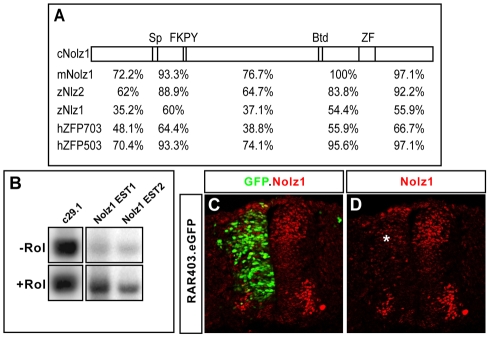
Nolz1 expression is induced by RA signals in spinal cord explants. (A) Conserved domains between chick (c), mouse (m), zebrafish (z) and human (h) predicted Nolz1 ORFs. Sp, Sp1-related domain; FKPY, putative Groucho consensus binding site; Btd, Drosophila Buttonhead domain; ZF, zinc-finger domain. Numbers indicate percentage identity in the regions between these domains. (B) Reverse northern of two different chick Nolz1 EST clones (EST1, EST2) probed with pools of cDNAs generated from St 19 ventral chick embryonic spinal cord explants grown in the presence (+) or absence (-) of retinol (Rol). c29.1 is a cDNA fragment from an unrelated gene known to be transcriptionally unresponsive to RA signals (Rao and Sockanathan, 2005). (C,D) Confocal images of chick spinal cords electroporated with RAR403 showing decreased dorsal Nolz1 expression (asterisk). Motoneurons are reduced as their generation is dependent on RA signaling.