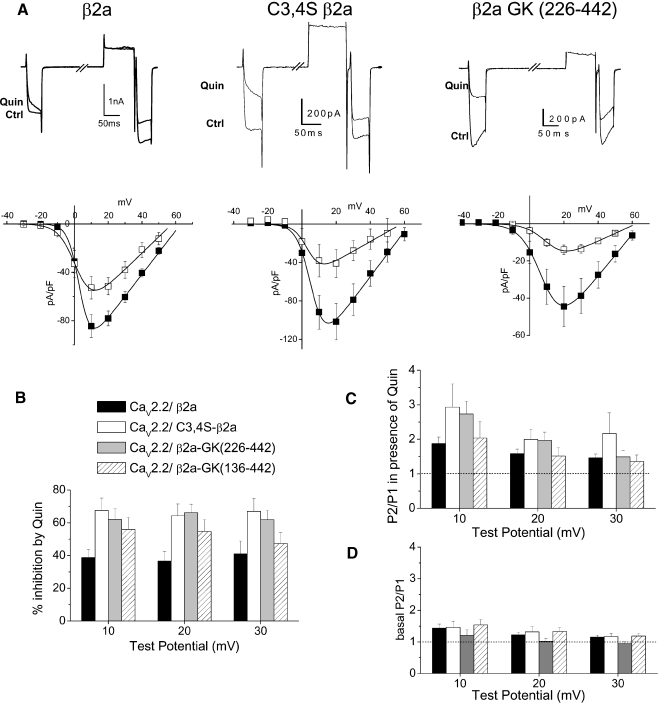
Fig. 3.
GK domains of β2a support voltage-dependent G protein modulation. aUpper panel example traces showing inhibition of CaV2.2 currents (Ctrl) by quinpirole (Quin, 100 nM) for CaV2.2/α2δ-2 coexpressed with β2a (left), C3,4S-β2a (center), and with β2a-GK (226–442) (right). Traces are shown for 40 ms depolarizations to +10 mV before and immediately after a depolarizing prepulse to +120 mV. Lower panel current–voltage relationships for the same conditions prior to (filled squares) and during quinpirole application (open squares), (n = 6, 6, and 7, respectively). b Percentage inhibition by quinpirole between +10 and +30 mV for the three conditions depicted in a and the additional GK domain construct β2a-GK (136–442) (n = 9, 7, 11, and 11, respectively). c Facilitation (P2/P1) ratio between +10 and +30 mV in the presence of quinpirole for the three conditions depicted in a and β2a-GK (136–442) (n = 7, 8, 9, and 6, respectively). The dotted line indicates a P2/P1 ratio of 1. d Basal facilitation (P2/P1) ratio between +10 and +30 mV for the three conditions depicted in a and β2a-GK (136–442) (n = 7, 9, 10, and 9, respectively). The dotted line indicates a P2/P1 ratio of 1