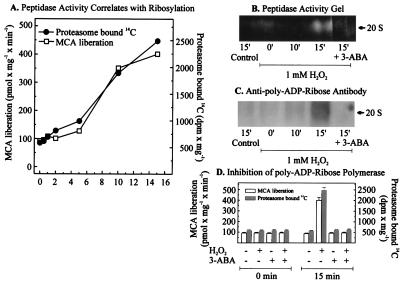
Figure 4.
Poly-ADP ribosylation of the proteasome in nuclei of K562 human hematopoietic cells after hydrogen peroxide treatment increases its activity. (A) Proteasome peptidase activity correlated with the degree of poly-ADP ribosylation, measured as incorporated 14C from 14C-NAD+ after bolus addition of 1 mM hydrogen peroxide to isolated nuclei from K562 cells. Nuclei of K562 cells were isolated by a modified method of Emig et al. (20) and incubated with 1 mM hydrogen peroxide in 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.8), 200 μM NAD+, 10 mM MgCl2, and 5 mM DTT, containing 10,000 dpm 14C-labeled NAD+. (B and C) The analysis of lysates from K562 cell nuclei after H2O2 treatment. The lysates were analyzed by nondenaturing one-dimensional polyacrylamide electrophoresis according to ref. 21. (B) An activity staining and (C) an immunoblot of the proteasome, using an anti-poly-ADP ribose antibody (Biomol, Plymouth Meeting, PA). (D) The effect of 3-ABA on the proteasome activity and the [14C] incorporation, after hydrogen peroxide treatment. Experimental conditions were as in Fig. 3A except for the use of 3-ABA (1 mM).