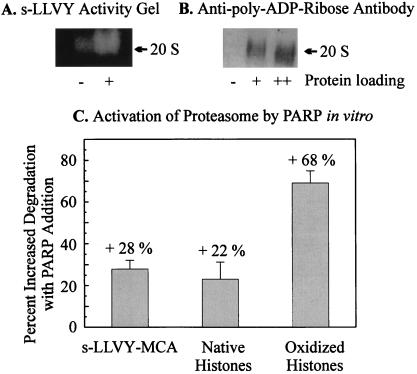
Figure 5.
Activation of the isolated 20S proteasome by in vitro poly-ADP ribosylation. (A) Activation of the isolated 20S proteasome after in vitro poly-ADP ribosylation. In vitro poly-ADP ribosylation of the 20S proteasome was performed according to Banasik et al. (27). Purified proteasome (0.15 mg/ml) was incubated with 1 μg/ml of PARP and 10 μg/ml of DNA (sonicated 10 times for 20 s) in a medium consisting of 100 mM Tris, 200 μM NAD+, 10 mM MgCl2, and 5 mM DTT. Controls were incubated without NAD+. After 10 min the reaction was stopped by addition of 1 mM 3-ABA, and the mixture was rapidly cooled on ice. Peptidase activity was determined after nondenaturing one-dimensional polyacrylamide electrophoresis as described in Fig. 4. (A) The activation of the peptidase activity of the proteasome after overlaying the gel with 200 μM suc-LLVY-MCA. (B) The immunoblot analysis of the gel after blotting on a nitrocellulose membrane by using the anti-ADP ribose antibody (Biomol) used in Fig. 4. The lanes indicated by + and ++ are the same probes loaded with different amounts of protein. Proteolytic activities in C were analyzed before and after in vitro poly-ADP ribosylation, using undamaged and H2O2-modified histones and the peptide suc-LLVY-MCA as substrates (see Figs. 1–4).