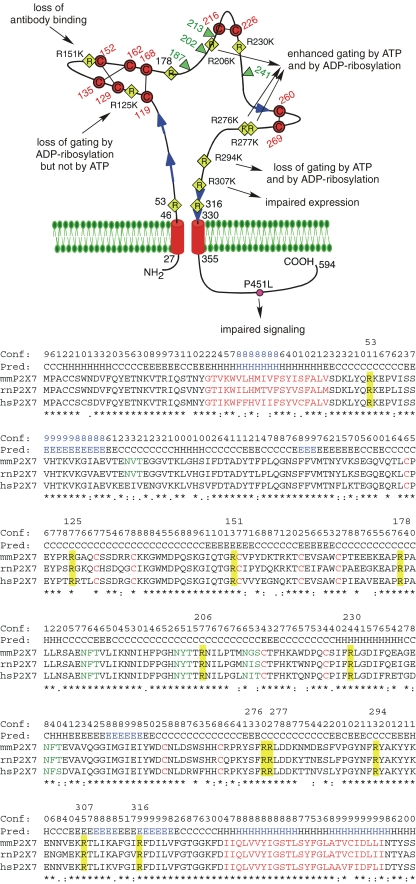
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the functional consequences following substitution of the conserved arginine residues in the ectodomain of mouse P2X7. The connectivity of cysteine residues (in red) corresponds to that proposed for P2X1 and P2X2 [6]. The conserved arginine (R) residues in the ectodomain are indicated by yellow diamonds, the natural allelic polymorphism in the cytosolic domain [70] that distinguishes C57BL/6 mice from wild-type mice is indicated by a pink circle. Potential glycosylation sites are indicated by green triangles and predicted β-strands by blue arrows. The sequences in the alignment of mouse, rat, and human P2X7 are truncated five residues downstream of Tm2. Secondary structures predicted with PSIPRED [49] are indicated above the alignment (H helix; E extended β-strand; C coil, unstructured). Structure units with a confidence >8 are highlighted in blue. Identical, strongly and weakly conserved amino acid residues are indicated by asterisk and colon. Predicted transmembrane domains and conserved cysteine residues are in red, potential N-linked glycosylation sites are in green. The 11 conserved arginine residues in the ectodomain are highlighted in yellow and their positions in residue number (for mouse P2X7) are indicated above the alignment