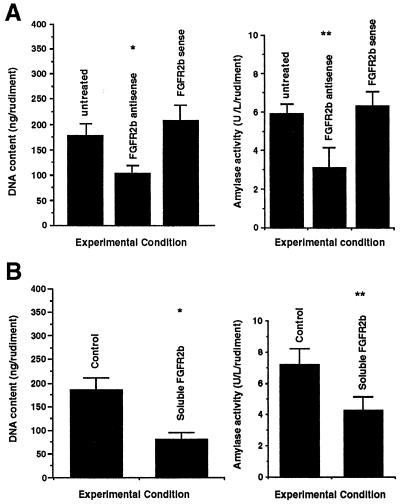
Figure 6.
Effects of the abrogation of FGFR2b signaling pathway on the development in vitro of E11.5 pancreatic rudiments (epithelium + mesenchyme). (A) E11.5 pancreatic rudiments were cultured in serum-free medium in the presence of antisense and sense FGFR2b oligonucleotides or in the absence of oligonucleotides. After 7 days in culture, the DNA content and amylase activity per rudiment were analyzed. As shown, treatment with antisense FGR2b oligonucleotides provokes a 2-fold decrease in both DNA (∗, P < 0.01)and amylase activity (∗∗, P < 0.01). At least five rudiments were used for each experiment. The concentration of oligonucleotides was 30 mM. (B) Similar results were obtained when pancreatic rudiments were cultured in the presence of recombinant soluble FGFR2b.