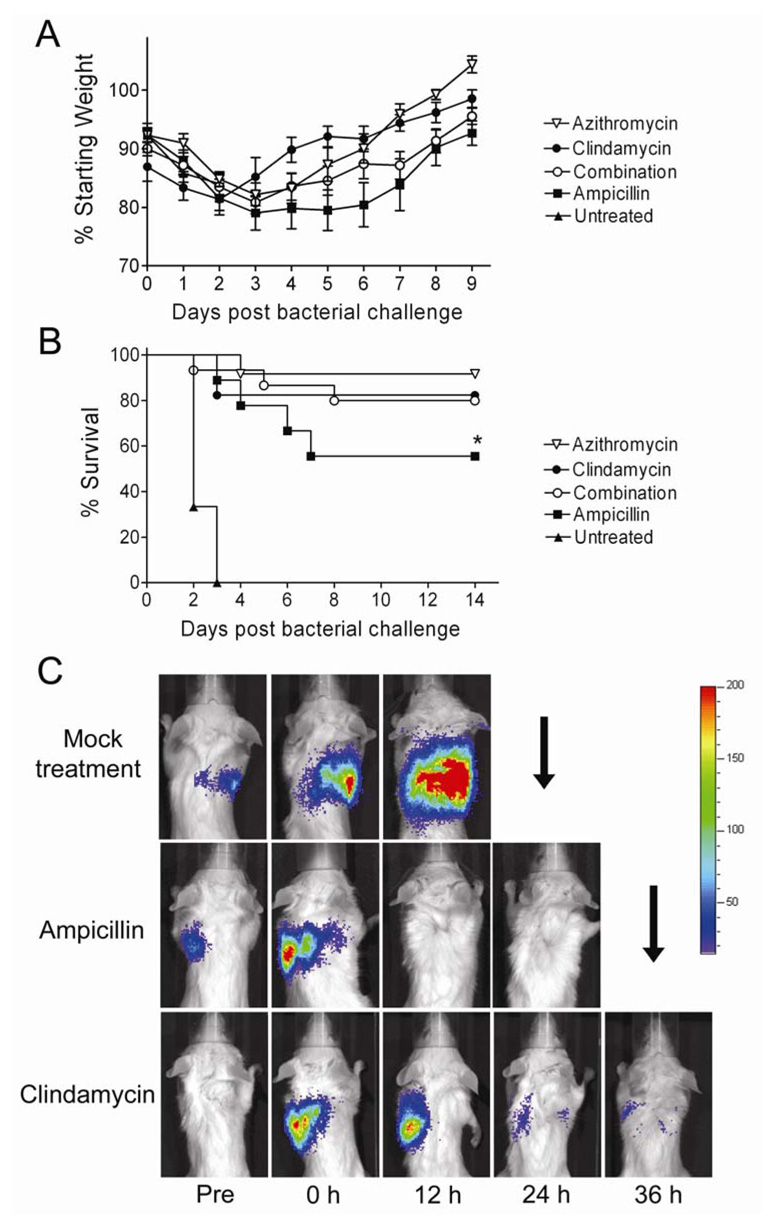
Figure 2.
Survival of mice treated for secondary bacterial pneumonia with a cell wall active agent or protein synthesis inhibitors. Groups of mice were infected with influenza virus PR8 then challenged 7 days later with S. pneumoniae and monitored for development of pneumonia by bioluminescent imaging (defined as a flux of light through the thorax of > 22,000 RLU per minute). Treatment with azithromycin (n=12), clindamycin (n=17), a combination of clindamycin for 24 hours followed by clindamycin plus ampicillin (n=15), ampicillin alone (n=9) or mock treatment (n=6) was initiated after development of pneumonia. A) Weight loss and B) survival are plotted. Error bars indicate the s.d. of the mean weights. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05) compared to all other groups by the Log Rank test on the Kaplan-Meier survival data. C) Representative pictures from bioluminescent imaging of mice with pneumonia before (Pre) development of pneumonia, at the initiation of treatment (o h), and 12, 24 and 36 hours after treatment starts. The scale at the right indicates RLU per pixel. A down-going arrow indicates death of the animal prior to that imaging timepoint.