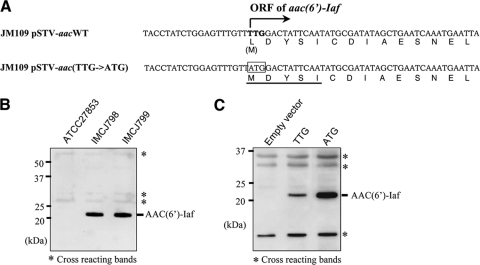
FIG. 5.
Production of AAC(6′)-Iaf in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates and E. coli transformants used in aminoglycoside susceptibility tests. Each lysate was separated by SDS-15% PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using polyclonal anti-AAC(6′)-Iaf antibodies. The positions of nonspecifically reacting protein bands serving as loading controls are indicated by asterisks. (A) Partial sequences of the aac(6′)-Iaf gene and its promoter region on pSTV-aacWT and pSTV-aac(TTG→ATG) and of the corresponding peptides. The putative wild-type initiation codon is shown in boldface type. The initiation codon altered to ATG is boxed. The N-terminal sequence of native AAC(6′)-Iaf, as determined by the Edman degradation method, is underlined. (B) Expression of AAC(6′)-Iaf in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates IMCJ798 and IMCJ799. (C) Expression of AAC(6′)-Iaf in E. coli JM109 carrying pSTV28 (lane 1; empty vector), pSTV-aacWT (lane 2; TTG), and pSTV-aac(TTG→ATG) (lane 3; ATG).