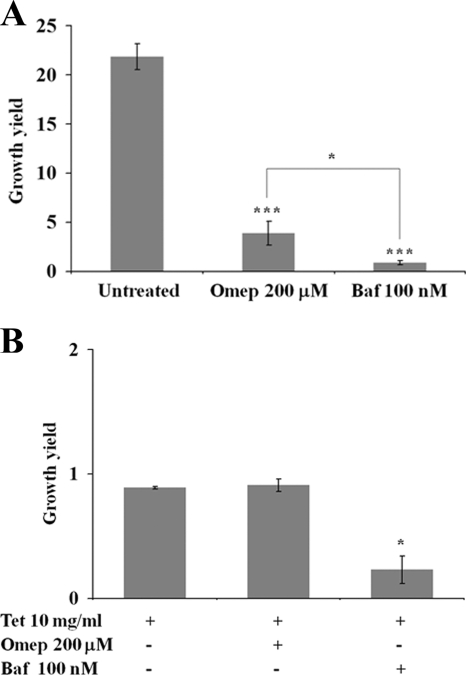
FIG. 3.
Proton pump inhibitors differently affect the viability of intracellular S. Typhimurium. (A) Bafilomycin A1 had a stronger inhibitory effect on the intracellular replication of S. Typhimurium in RAW264.7 cells. (B) RAW264.7 cells infected with S. Typhimurium 14028 were treated simultaneously with tetracycline (10 μg/ml) to cause a reversible inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis and replication, in conjunction with either omeprazole (Omep) or bafilomycin A1 (Baf). This analysis showed that tetracycline completely inhibited bacterial intracellular replication, and that there was no additive effect by combining omeprazole and tetracycline (Tet). In contrast, bafilomycin A1 caused a significant decrease in the numbers of tetracycline-treated bacteria. The statistical difference between the growth yields was confirmed in a paired student's t test (*, P < 0.05).