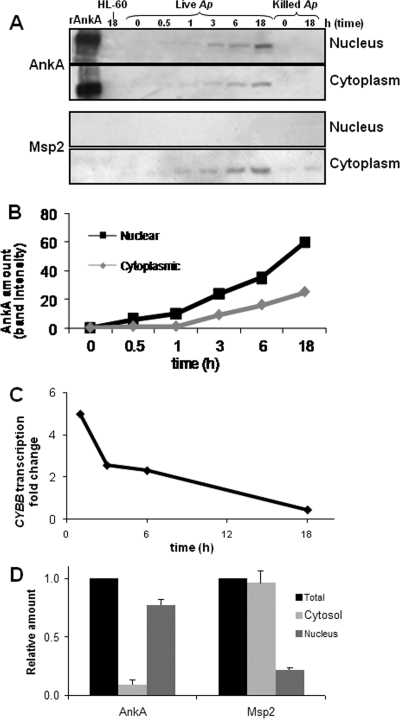
FIG. 1.
AnkA accumulates in nuclei of infected granulocytes as host transcriptional changes associated with A. phagocytophilum infection occur. (A) HL-60 cells were exposed to live or heat-killed A. phagocytophilum, and samples of cells were collected at different time points, fractionated, and analyzed for the presence of AnkA or Msp2 proteins in the nuclear and cytosolic fractions. (B) The amounts of AnkA in nuclei and cytosol of infected HL-60 cells were calculated by densitometry of the AnkA bands (a representative example of more than three replicate experiments is shown). (C) CYBB transcription levels over time were quantitated by qRT-PCR normalized to ACTB. (D) Neutrophils infected in culture with A. phagocytophilum were collected at 24 h postinfection and fractionated; total cell lysate, nuclear extract, and cytoplasm were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and reacted with AnkA-specific MAb or Msp2 MAb; and densitometric analysis of the bands was performed. Protein amounts in each fraction were normalized to the amount present in the total cell lysate. Shown are the results of three densitometric determinations as means ± standard errors.