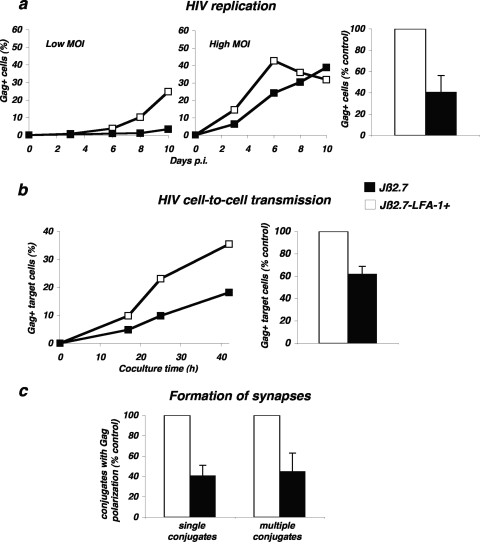
FIG. 6.
Role of LFA-1 during HIV replication and cell-to-cell transfer. (a) HIV replication is impaired in LFA-1-defective Jurkat cells. Cells of the Jurkat derivative Jβ2.7 (which lacks LFA-1) and Jβ2.7-LFA-1+ cells were exposed to HIV (NL4-3 strain), at either a low (5 ng/106 cells/ml) or high (50 ng/106 cells/ml) MOI. Viral replication was followed by measuring the percentage of Gag+ cells by flow cytometry at the indicated days postinfection (p.i.). A representative experiment is shown in the left panel. The mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments is depicted in the right panel, with 100% corresponding to values obtained in Jβ2.7-LFA1+ cells at the peak at all MOIs. (b) HIV cell-to-cell transfer analyzed by flow cytometry. Productively HIV-infected Jβ2.7-LFA1+ and Jβ2.7 cells (about 25% Gag+) were cocultivated with target CFSE+ Jurkat cells at a 1/10 ratio. The percentage of Gag+ cells among targets (CFSE+) is shown at the indicated times of coculture. A representative experiment is shown on the left. The mean ± standard deviation of four independent experiments (16-h time point, with the donor/recipient ratio varying from 1/3 to 1/10) is depicted in the right panel, with 100% corresponding to values obtained in Jβ2.7-LFA1+ cells. (c) Formation of single VS and polysynapses. Productively HIV-infected Jβ2.7-LFA1+ and Jβ2.7 cells (about 25 to 40% Gag+) were cocultivated for 1 h with the target Far Red dye-labeled Jurkat cells. Single and multiple conjugates displaying Gag clustering at the junction zone with targets were scored. Data are means ± standard deviations of four independent experiments, with 100% corresponding to values obtained in Jβ2.7-LFA1+ cells (with totals of 535 Jβ2.7-LFA1+ and 592 Jβ2.7-infected cells analyzed).