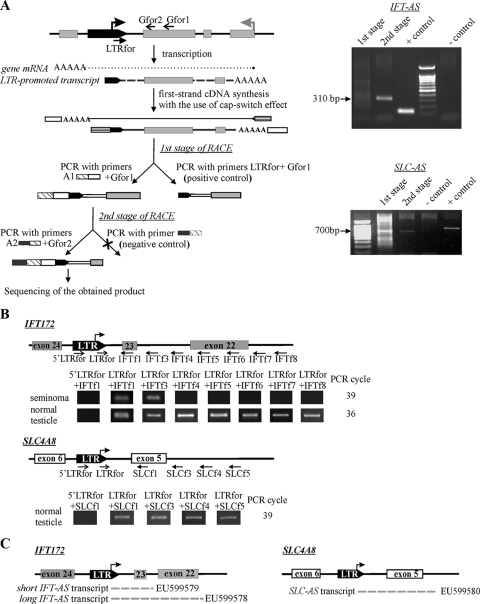
FIG. 2.
(A) Scheme of the 5′RACE technique and its results for the IFT-AS and SLC-AS transcripts. 5′RACE was performed according as described previously (61). The gray arrow indicates the gene transcriptional start site, and the black arrow indicates the transcriptional start site within LTR. White and striped rectangles represent adapter sequences used for cDNA synthesis. cDNA synthesized using the “cap-switch” effect was used as a template for RACE. To achieve the required specificity, the reaction was performed in two stages. In the first PCR, we used a gene-specific primer (Gfor1), complementary to SLC exon 5 or IFT172 exon 23, and the suppression adapter A1, whose 3′-half was complementary to the sequence of the oligonucleotide used for cDNA synthesis. The second PCR was performed with the nested gene-specific primer Gfor2 and the “step-out” suppression adapter A2. Suppression adapters were used to prohibit the amplification of molecules that do not contain annealing site for a gene-specific primer. (B) The extent of the antisense transcripts was determined in a series of qRT-PCRs with pairs of primers, one of which was complementary to the 3′ sequence of the LTR (LTRfor) and the others of which were complementary to different positions within the gene. RT-PCR product size for the primers LTRfor+IFT172for1/IFT172for3-for8 corresponded to theoretically expected lengths of 123, 292, 326, 428, 527, 626, and 712 bp, respectively. The lengths of the RT-PCR products with the primers LTRfor+SLC4A8for1/SLC4A8for3-for5 were 820, 926, 1,050, and 1,155 bp, respectively. To validate 5′RACE data and measure the level of the potential readthrough transcripts initiated somewhere upstream of the LTRs, qRT-PCRs with the primers 5′LTRfor+IFT172for1 or SLC4A8for1 were performed. (C) Types of antisense transcripts found and their corresponding accession numbers.