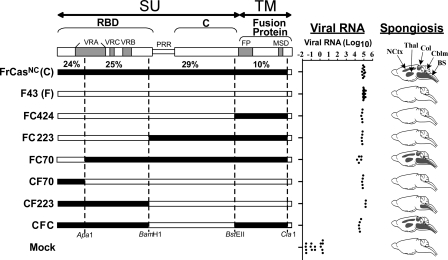
FIG. 2.
Neurovirulence is determined by the RBD of CasBrE. Schematic diagrams are shown of the envelope precursor polyproteins (pr85env) of chimeric viruses that exhibited neuroinvasiveness comparable to that of FrCasNC. The boundaries of the surface glycoprotein (SU) and the transmembrane protein (TM) are shown at the top. The brackets denote the boundaries of the domains of the SU protein. The RBD and C-terminal domain (C) are linked by a PRR hinge. Subdomains are shown as gray bars and include the variable regions of SU (VRA, VRC, and VRB) and the fusion peptide (FP) and membrane-spanning domain (MSD) of the TM protein. The numbers just above the diagram of FrCasNC represent the percent difference in the amino acid sequence between FrCasNC and F43 for each restriction enzyme fragment. The dotted lines show the restriction sites used to construct these chimeric envelope genes. Viral RNA was determined at 17 to 20 dpi by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR on RNA extracted from brainstems of mice inoculated intraperitoneally with each virus. Each dot represents a mouse. The distribution of spongiform lesions is shown as dark gray areas in diagrams of parasaggital sections of brains (under the column heading “Spongiosis”). The names of each affected region is shown for the brain of FrCasNC and include brainstem (BS), deep cerebellar nuclei (Cblm), anterior and posterior colliculi (Col), thalamus (Thal), and deep neocortex (NCtx). Histopathology was assessed on no fewer than three mice per group at 17 to 20 dpi.