FIG. 6.
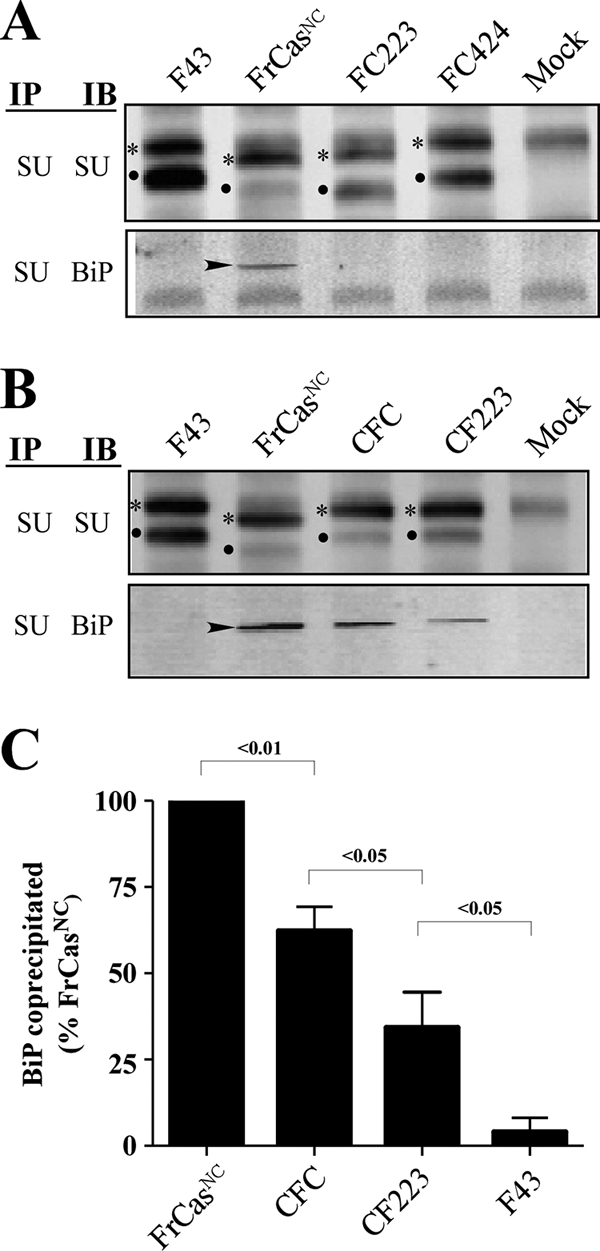
Both folding instability and ER retention were determined by the RBD of FrCasNC. NIH 3T3 cells were infected with F43, FrCasNC, and the chimeric viruses shown in Fig. 4. (A) Western blots of lysates from cells infected with viruses containing the RBD of F43 (FrCasNC served as a positive control). (B) Western blots of lysates from cells infected with viruses containing the RBD of FrCasNC (F43 served as a negative control). Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-SU antiserum and immunoblotted with either anti-SU or anti-BiP, as described in the legend to Fig. 5. The two deletions in PRR of the CasBrE envelope protein accounts for the differences in size of the envelope proteins of these viruses. Thus, viruses containing the PRR of F43 (FC424, CF223, and CFC) have envelope proteins of comparable molecular size to F43. The virus FC223 contains the PRR of CasBrE, and its envelope proteins are comparable in size to those of FrCasNC. The relative ratios of pr85env (asterisks) and SU protein (dots) suggest that, like the envelope protein of FrCasNC, the envelope proteins of CFC and CF223 were retained in the ER. In addition, like FrCasNC, BiP (arrowheads) was coprecipitated with the envelope proteins of CFC and CF223, both of which contain the RBD of FrCasNC (see Fig. 4). For viruses that exhibited detectable BiP binding, the relative levels of BiP coprecipitated with anti-SU is shown in panel C. Pixel density was normalized to total pr85env in each lysate and expressed as a percentage of BiP coprecipitated in lysates of FrCasNC-infected cells. The results are cumulative data from three independent experiments. The numbers above each bracket represents the P values calculated by using one-way ANOVA (repeat measures test).
