FIG. 1.
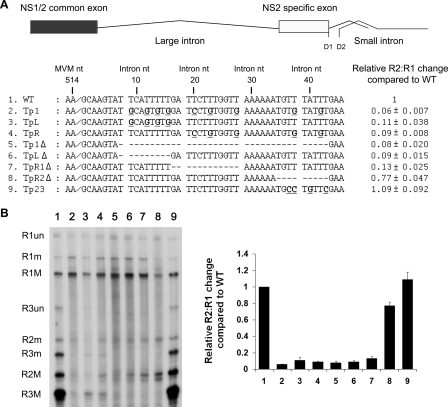
U- and A-rich intronic sequences immediately downstream of the 5′ splice site of the MVM large intron are required for its efficient excision. (A) Diagram of the R2 transcript and the DNA region just downstream of the large-intron donor, showing changes (bold and underlined) or deletions (dashed lines) in the U-rich regions (slashes indicate the 5′ cleavage site between nts 514 and 515 of the published sequence) of the various mutants, as described in the text. MVM and intron numbering is shown. RNase protection analyses quantified using Fujifilm MultiGauge software and performed as described in the text, using an antisense probe spanning nt 1858 to 2377, were used to quantify RNAs generated following transfection of each mutant (as described in the text); the results are shown to the right. Data from at least three experiments, with standard deviations, are presented as the relative R2:R1 changes compared to that of the wild type (WT). (B) Representative RNase protection assay. The identities of the RNA species are given on the left. M, usage of small intron D1 at nt 2280; m, usage of small-intron donor D2 at nt 2317; un, RNA remaining unspliced through the probe region. A graphic analysis of the quantification data shown in panel A is presented in the right panel. (C) Diagram of the DNA region just downstream of the large-intron donor, showing changes (bold and underlined) or deletions (dashed lines) in the A-rich region (slashes indicate the 5′ cleavage site between nts 514 and 515 of the published sequence) of the various mutants, as described in the text. MVM and intron numbering is shown. (D) Left panel: representative RNase protection analysis of RNAs generated from constructs shown in panel C, using a probe spanning nt 1858 to 2377. Right panel: quantification of RNase protection. Data from at least three experiments, with standard deviations, are presented in tabular (bottom) and graphical (top) forms as relative R2:R1 changes compared to that of the wild type. (E) Quantification of RNase protection of constructs, indicated by using probe-spanning nt 1858 to 2377. CD1 refers to consensus donor mutation 1 (see text). The quantifications include data from at least three experiments, with standard deviations, and are presented as relative R2:R1 changes compared to that of the wild type.