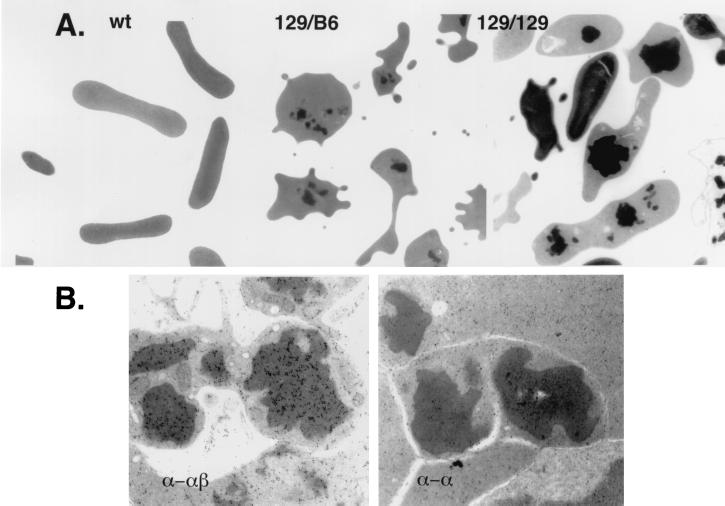
Figure 2.
Electron microscopic and immunoelectron microscopic analyses of red blood cell inclusion bodies. (A) Left to Right, wild-type (wt) and thalassemic red blood cells derived from mice bearing the indicated β-globin allele, 129/B6 (129sv/ev/C57BL/6) and 129/129 (129sv/ev/129sv/ev). The inclusion bodies are the readily visible electron-dense structures. Magnification ×7,000 (Left), ×6,000 (Center), and ×6000 (Right). (B) Shown are inclusions from sections of marrow from an α-thalassemic mouse bearing the 129sv/ev/129sv/ev β-globin alleles. The sections were immunogold-labeled with polyclonal antibody directed against hemoglobin (both α- and β-chains) (α-αβ) and antibody directed only against purified α-chain (α-α). Magnification is ×26,000. Inclusions show a positive reaction with the antibody against hemoglobin but are not reactive with the antibody against α-globin chains.