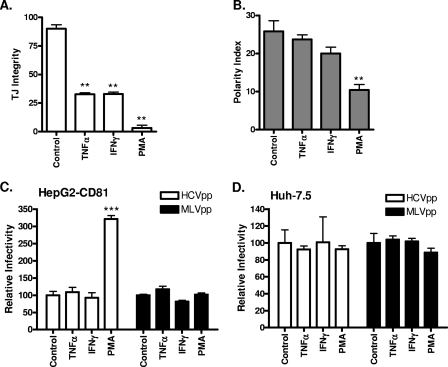
FIG. 7.
Effect(s) of proinflammatory cytokines on HepG2 TJ integrity, polarity, and HCV entry. HepG2-CD81 cells were treated with the control (DMSO; 1:1,000), TNF-α (10 ng/ml), IFN-γ (10 ng/ml), or PMA (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. (A) Cells were incubated with CMFDA at 37°C for 10 min and washed, and the capacity of BC lumens to retain CMFDA was monitored by using fluorescence microscopy. TJ integrity was assessed as the percentage of total BC retaining CMFDA (triplicate coverslips, five fields of view per coverslip). **, P < 0.001 (t test). (B) Cells were fixed, and the number of MRP2-positive BC per 100 cell nuclei was counted (polarity index). HCVpp (white bars) and MLVpp (black bars) infection of control-, TNF-α-, IFN-γ-, or PMA-treated HepG2-CD81 (C) or Huh-7.5 (D) cells is shown relative to control cells ± SD. ***, P < 0.001 (t test). HCVpp infectivity values for HepG2-CD81, HepG2, and Huh-7.5 cells were 48,350 ± 1,240 RLU, 313 ± 29 RLU, and 149,194 ± 9,869 RLU, respectively. MLVpp infectivity values for HepG2-CD81, HepG2, and Huh-7.5 cells were 349,990 ± 7,075 RLU, 358,400 ± 18,162 RLU, and 727,454 ± 11,673 RLU, respectively.