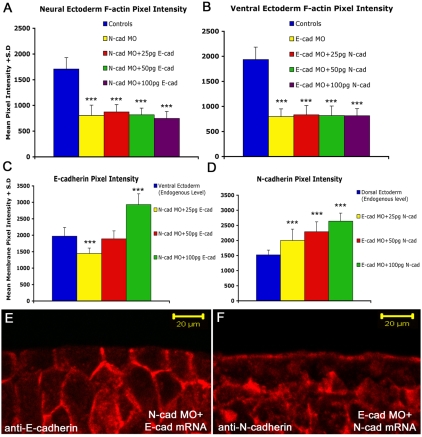
Fig. 9.
N- and E-cadherin may not rescue each other because they localize to different regions of the ectodermal cells. (A) Levels of cortical F-actin in the neural ectoderm in controls, N-cadherin-depleted and N-cadherin-depleted followed by three different doses of E-cadherin mRNA. Cortical actin is not rescued by any dose of E-cadherin mRNA. (B) The converse experiment compares the cortical actin levels in non-neural ectoderm of control, E-cadherin-depleted and N-cadherin depleted followed by three doses of N-cadherin mRNA. Cortical actin is not rescued by any dose of N-cadherin mRNA. (C,D) The levels of E-cadherin and N-cadherin proteins in Xenopus embryos from the same experiment. In each case, translation is efficient and generates at least as much protein as found in the control tissues. ***Statistically significant difference between the control (blue) and labeled bar (P<0.001). (E,F) The location of E-cadherin expressed in N-cadherin-depleted neural ectoderm (E), and N-cadherin expressed in E-cadherin-depleted non-neural ectoderm (F). E-cadherin is expressed basolaterally in the neural ectoderm, whereas N-cadherin is concentrated apically in the non-neural ectoderm. Scale bars: 20 μm.