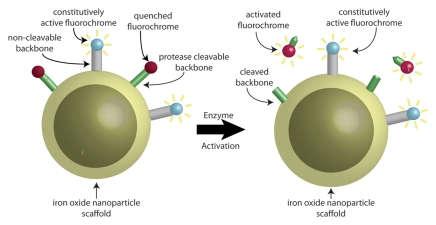
Figure 1b:
Schematic representations of dual fluorescence correction method. (a) Dual fluorescence correction method is applied to endovascular imaging of vascular disease. Endovascular imaging catheter introduced into blood vessel collects fluorescent photons from two-fluorochrome (F1 and F2) molecular probe (shown in b). Using ratio of fluorescence signals from the two fluorochromes with real-time computer-based algorithm (additional hardware not shown) enables in vivo imaging of NIR fluorescence in vascular lesions, despite attenuating effects of intervening blood. (b) Design of two-fluorochrome molecular probe used to image protease activity consists of iron oxide nanoparticle scaffold, onto which two fluorochromes that fluoresce at distinct wavelengths are attached. One fluorochrome (blue) is constitutively active and bound to a noncleavable peptide backbone. The second fluorochrome (red) is quenched initially; however, it regains its fluorescence properties and becomes activated after protease cleavage of the peptide backbone to which it is attached. By using the ratio of activatable fluorochrome signal to constitutively active fluorochrome signal, one can measure the enzyme activity in vascular lesions through blood.