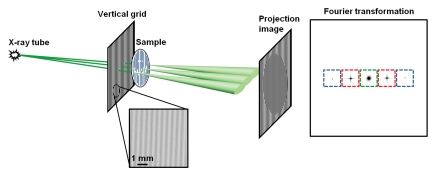
Figure 1a:
Schematic illustration of Fourier x-ray scattering imaging with (a) vertical grid or (b) horizontal grid. (a) Cone beam from x-ray tube is amplitude modulated by vertical grid before illumination of a sample of vertical fibrous composition. X-ray scattering in sample is broadest in plane perpendicular to the fibers and results in substantial blurring of the grid shadows on the projection image. Fourier transformed image contains zero-order (green) peak, which is not modulated by the grid, and first-order (red) and second-order (blue) modulated signals. The color boxes mark the mask filters used to obtain the smaller images corresponding to the peaks. (b) In experiment similar to that illustrated in a but with horizontal grid, the sample scatters x-rays weakly in vertical direction to result in less blurring of grid shadows. Zero-order and higher-order peaks, and their corresponding mask filters, are arrayed in vertical direction in Fourier space. D1 = distance between x-ray source and grid, D2 = distance between grid and sample, D3 = distance between sample and camera.